Page 19 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 19
LOS 34.j: Explain traditional theories of the term READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
structure of interest rates and describe the INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
implications of each theory for forward rates and MODULE 34.5: TERM STRUCTURE THEORY
the shape of the yield curve.
Unbiased (Pure) Expectations Theory: An investor with a three-year investment horizon expects or would be indifferent
between investing in a three-year bond or in a five-year bond that will be sold two years prior to maturity.
In other words, forward rates are solely a function of expected future spot rates, and that every maturity strategy has the same
expected return over a given investment horizon.
The underlying principle is risk neutrality: Investors don’t demand a risk premium for maturity strategies that differ from their
investment horizon.
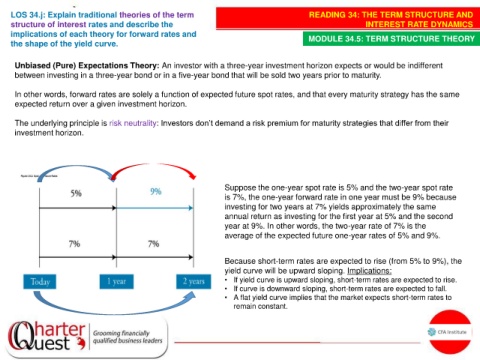
Suppose the one-year spot rate is 5% and the two-year spot rate
is 7%, the one-year forward rate in one year must be 9% because
investing for two years at 7% yields approximately the same
annual return as investing for the first year at 5% and the second
year at 9%. In other words, the two-year rate of 7% is the
average of the expected future one-year rates of 5% and 9%.
Because short-term rates are expected to rise (from 5% to 9%), the
yield curve will be upward sloping. Implications:
• If yield curve is upward sloping, short-term rates are expected to rise.
• If curve is downward sloping, short-term rates are expected to fall.
• A flat yield curve implies that the market expects short-term rates to
remain constant.