Page 22 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 22
LOS 34.k: Describe modern term structure READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
models and how they are used. INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
MODULE 34.6: INTEREST RATE MODELS
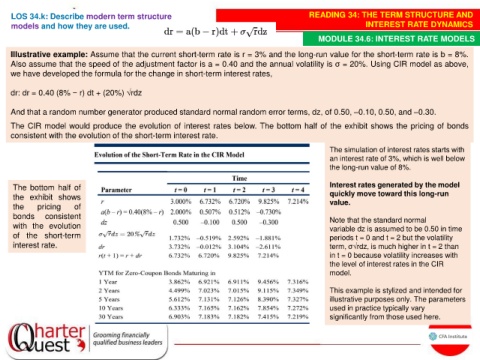
Illustrative example: Assume that the current short-term rate is r = 3% and the long-run value for the short-term rate is b = 8%.
Also assume that the speed of the adjustment factor is a = 0.40 and the annual volatility is σ = 20%. Using CIR model as above,
we have developed the formula for the change in short-term interest rates,
dr: dr = 0.40 (8% − r) dt + (20%) √rdz
And that a random number generator produced standard normal random error terms, dz, of 0.50, –0.10, 0.50, and –0.30.
The CIR model would produce the evolution of interest rates below. The bottom half of the exhibit shows the pricing of bonds
consistent with the evolution of the short-term interest rate.
The simulation of interest rates starts with
an interest rate of 3%, which is well below
the long-run value of 8%.
The bottom half of Interest rates generated by the model
the exhibit shows quickly move toward this long-run
value.
the pricing of
bonds consistent Note that the standard normal
with the evolution variable dz is assumed to be 0.50 in time
of the short-term periods t = 0 and t = 2 but the volatility
interest rate. term, σ√rdz, is much higher in t = 2 than
in t = 0 because volatility increases with
the level of interest rates in the CIR
model.
This example is stylized and intended for
illustrative purposes only. The parameters
used in practice typically vary
significantly from those used here.