Page 35 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 35
LOS 35.d: Describe the backward induction valuation READING 35: THE ARBITRAGE-FREE VALUATION FRAMEWORK
methodology and calculate the value of a fixed-income
instrument given its cash flow at each node.
MODULE 35.1: BINOMIAL TREES, PART 1
The process of valuing a bond using a binomial interest rate tree. Backward because in order
to determine the value of a bond today at Node 0, you need to know the values that the bond
can take at the Year 1 node. But to determine the values of the bond at the Year 1 nodes, you
need to know the possible values of the bond at the Year 2 nodes. Thus, for a bond that has N
compounding periods, the current value of the bond is determined by computing the bond’s
possible values at Period N and working backwards to Node 0.
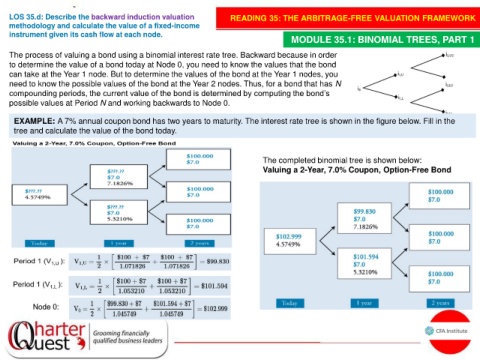
EXAMPLE: A 7% annual coupon bond has two years to maturity. The interest rate tree is shown in the figure below. Fill in the
tree and calculate the value of the bond today.
The completed binomial tree is shown below:
Valuing a 2-Year, 7.0% Coupon, Option-Free Bond