Page 48 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 48
LOS 36.g: Explain the calculation and
use of option-adjusted spreads. READING 36: VALUATION AND ANALYSIS: BONDS WITH EMBEDDED OPTIONS
OAS is a constant spread added to the risk-free rate used to value gov’t MODULE 36.4: OPTION-ADJUSTED SPREAD
bonds (in the backward induction BIRT valuation approach, to account
for the extra credit risk applicable to valuing a risky corporate bond.
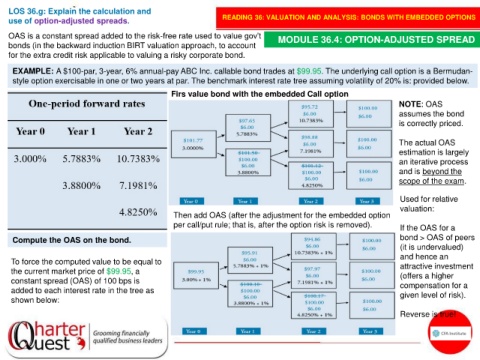
EXAMPLE: A $100-par, 3-year, 6% annual-pay ABC Inc. callable bond trades at $99.95. The underlying call option is a Bermudan-
style option exercisable in one or two years at par. The benchmark interest rate tree assuming volatility of 20% is: provided below.
Firs value bond with the embedded Call option
NOTE: OAS
assumes the bond
is correctly priced.
The actual OAS
estimation is largely
an iterative process
and is beyond the
scope of the exam.
Used for relative
valuation:
Then add OAS (after the adjustment for the embedded option
per call/put rule; that is, after the option risk is removed). If the OAS for a
Compute the OAS on the bond. bond > OAS of peers
(it is undervalued)
and hence an
To force the computed value to be equal to attractive investment
the current market price of $99.95, a (offers a higher
constant spread (OAS) of 100 bps is compensation for a
added to each interest rate in the tree as given level of risk).
shown below:
Reverse is true!