Page 49 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 49
LOS 36.h: Explain how interest rate volatility
affects option-adjusted spreads. READING 36: VALUATION AND ANALYSIS: BONDS WITH EMBEDDED OPTIONS
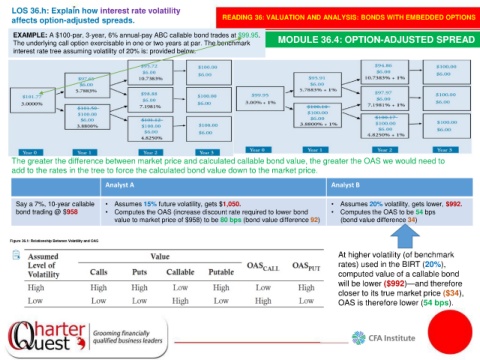
EXAMPLE: A $100-par, 3-year, 6% annual-pay ABC callable bond trades at $99.95. MODULE 36.4: OPTION-ADJUSTED SPREAD
The underlying call option exercisable in one or two years at par. The benchmark
interest rate tree assuming volatility of 20% is: provided below.
The greater the difference between market price and calculated callable bond value, the greater the OAS we would need to
add to the rates in the tree to force the calculated bond value down to the market price.
Analyst A Analyst B
Say a 7%, 10-year callable • Assumes 15% future volatility, gets $1,050. • Assumes 20% volatility, gets lower, $992.
bond trading @ $958 • Computes the OAS (increase discount rate required to lower bond • Computes the OAS to be 54 bps
value to market price of $958) to be 80 bps (bond value difference 92) (bond value difference 34)
At higher volatility (of benchmark
rates) used in the BIRT (20%),
computed value of a callable bond
will be lower ($992)—and therefore
closer to its true market price ($34),
OAS is therefore lower (54 bps).