Page 24 - FUNDAMENTALS OF COMPUTER
P. 24
24 Fundamentals of Computers NPP
other register. Normally the register holding h¡Ÿ& gm_mÝ`V`m EŠ`yå`yboQ>a Zm_H$ a{OñQ>a _| n[aUm_
the result is called accumulator. S>mbm OmVm h¡Ÿ&
Registers
CU
ALU Timing Signals
CU (Control Unit) NPP CU (H§$Q´>mob `y{ZQ>)
Control unit controls all units and blocks H$åß`yQ>a Ho$ gmao I§S> d BH$mB©`m± H§$Q´>moc `y{ZQ> Ho$
of the computer system. The ALU performs an {Z`§ÌU _| hmoVo h¡Ÿ& Bggo {g¾b {_bZo na hr ALU H$m`©
operation when it receives control signal from
CU. The flow of binary number into and from g§nÝZ H$aVm h¡Ÿ& a{OñQ>a ‘| VWm a{OñQ>a go ~m¶Zar Zå~a
registers is under control of control unit. Input- H$m àdmh H$ÝQ´>mob ¶y{ZQ> Ho$ {Z¶§ÌU ‘| hmoVm h¡& BZnwQ>,
output devices and memory operation is also AmCQ>nwQ> VWm _o_moar H$s {H«$`mE± ^r BgHo$ {Z`§ÌU _|
controlled by this unit. It decides the sequence
of operations to be performed. Therefore the hmoVr h¡Ÿ& `hr BH$mB© {d{^ÝZ {H«$`mAm| H$m H«$_ V` H$aVr
signal originated from CU is called synchro- h¡Ÿ& AV… CU go {ZH$bZo dmbo {g¾bm| H$mo {gÝH«$moZmBqOJ
nising signal or timing signal. The position of
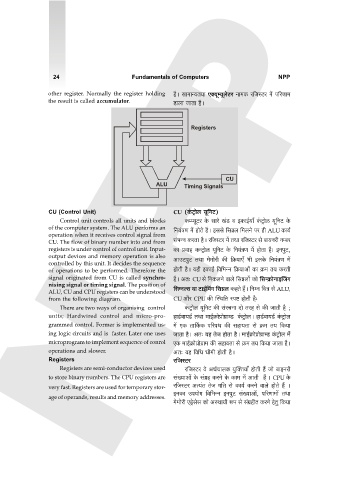
ALU, CU and CPU registers can be understood {g½Zëg ¶m Q>mB©q_J {g¾b H$hVo h¢Ÿ& {ZåZ {MÌ go ALU,
from the following diagram. CU Am¡a CPU H$s pñW{V ñnï> hmoVr h¡…
There are two ways of organising control H§$Q´>mob `y{ZQ> H$s g§aMZm Xmo Vah go H$s OmVr h¡ ;
units; Hardwired control and micro-pro- hmS>©dm`S>© VWm _mB©H«$moàmoJ«måS H§$Q´>mobŸ& hmS>©dm`S>© H§$Q´>mob
grammed control. Former is implemented us- _| EH$ Vm{H©$H$ n[anW H$s ghm`Vm go H«$_ V` {H$`m
ing logic circuits and is faster. Later one uses OmVm h¡Ÿ& AV… `h VoO hmoVm h¡Ÿ& _mB©H«$moàmoJ«måS> H§$Q´>mob _§|
microprogram to implement sequence of conrol EH$ _mB©H«$moàmoJ«m_ H$s ghm`Vm go H«$_ V` {H$`m OmVm h¡Ÿ&
operations and slower. AV… `h {d{Y Yr_r hmoVr h¡Ÿ&
Registers a{OñQ>a
Registers are semi-conductor devices used a{OñQ>a do AY©MmbH$ `wpŠV`m± hmoVr h¢ Omo ~mBZar
to store binary numbers. The CPU registers are g§»`mAm| Ho$ g§J«h H$aZo Ho$ H$m_ _| AmVr h¢ & CPU Ho$
very fast. Registers are used for temporary stor- a{OñQ>a AË`§V VoO J{V go H$m`© H$aZo dmbo hmoVo h¢ Ÿ&
age of operands, results and memory addresses. BZH$m Cn`moJ {d{^ÝZ BZnwQ> g§»`mAm|, n[aUm_m| VWm
‘o‘moar ES´>ogog H$mo AñWm¶r ê$n go g§J«hrV H$aZo hoVw {H$¶m