Page 57 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 57
CHAPTER 2 Diagnostic Tests for the Cardiovascular System 29
VetBooks.ir
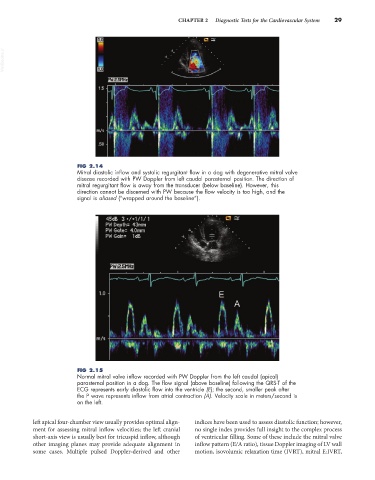
FIG 2.14
Mitral diastolic inflow and systolic regurgitant flow in a dog with degenerative mitral valve
disease recorded with PW Doppler from left caudal parasternal position. The direction of
mitral regurgitant flow is away from the transducer (below baseline). However, this
direction cannot be discerned with PW because the flow velocity is too high, and the
signal is aliased (“wrapped around the baseline”).
FIG 2.15
Normal mitral valve inflow recorded with PW Doppler from the left caudal (apical)
parasternal position in a dog. The flow signal (above baseline) following the QRS-T of the
ECG represents early diastolic flow into the ventricle (E); the second, smaller peak after
the P wave represents inflow from atrial contraction (A). Velocity scale in meters/second is
on the left.
left apical four-chamber view usually provides optimal align- indices have been used to assess diastolic function; however,
ment for assessing mitral inflow velocities; the left cranial no single index provides full insight to the complex process
short-axis view is usually best for tricuspid inflow, although of ventricular filling. Some of these include the mitral valve
other imaging planes may provide adequate alignment in inflow pattern (E/A ratio), tissue Doppler imaging of LV wall
some cases. Multiple pulsed Doppler-derived and other motion, isovolumic relaxation time (IVRT), mitral E:IVRT,