Page 370 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 370
336 Chapter 3
VetBooks.ir
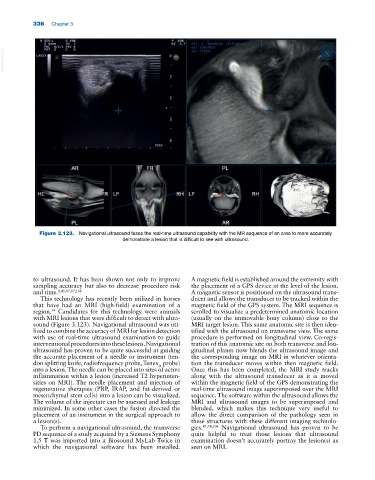
Figure 3.123. Navigational ultrasound fuses the real‐time ultrasound capability with the MR sequence of an area to more accurately
demonstrate a lesion that is difficult to see with ultrasound.
to ultrasound. It has been shown not only to improve A magnetic field is established around the extremity with
sampling accuracy but also to decrease procedure risk the placement of a GPS device at the level of the lesion.
and time. 1,45,47,87,106 A magnetic sensor is positioned on the ultrasound trans
This technology has recently been utilized in horses ducer and allows the transducer to be tracked within the
that have had an MRI (high‐field) examination of a magnetic field of the GPS system. The MRI sequence is
region. Candidates for this technology were animals scrolled to visualize a predetermined anatomic location
54
with MRI lesions that were difficult to detect with ultra (usually on the immovable bony column) close to the
sound (Figure 3.123). Navigational ultrasound was uti MRI target lesion. This same anatomic site is then iden
lized to combine the accuracy of MRI for lesion detection tified with the ultrasound on transverse view. The same
with use of real‐time ultrasound examination to guide procedure is performed on longitudinal view. Co‐regis
interventional procedures into these lesions. Navigational tration of this anatomic site on both transverse and lon
ultrasound has proven to be quite successful at guiding gitudinal planes now blends the ultrasound image and
the accurate placement of a needle or instrument (ten the corresponding image on MRI in whatever orienta
don splitting knife, radiofrequency probe, Tenex probe) tion the transducer moves within then magnetic field.
R
into a lesion. The needle can be placed into sites of active Once this has been completed, the MRI study tracks
inflammation within a lesion (increased T2 hyperinten along with the ultrasound transducer as it is moved
sities on MRI). The needle placement and injection of within the magnetic field of the GPS demonstrating the
regenerative therapies (PRP, IRAP, and fat‐derived or real‐time ultrasound image superimposed over the MRI
mesenchymal stem cells) into a lesion can be visualized. sequence. The software within the ultrasound allows the
The volume of the injectate can be assessed and leakage MRI and ultrasound images to be superimposed and
minimized. In some other cases the fusion directed the blended, which makes this technique very useful to
placement of an instrument in the surgical approach to allow the direct comparison of the pathology seen in
a lesion(s). these structures with these different imaging technolo
To perform a navigational ultrasound, the transverse gies. 45,54,106 Navigational ultrasound has proven to be
PD sequence of a study acquired by a Siemens Symphony quite helpful to treat those lesions that ultrasound
1.5 T was imported into a Biosound MyLab Twice in examination doesn’t accurately portray the lesion(s) as
which the navigational software has been installed. seen on MRI.