Page 384 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 384
350 Chapter 3
The diaphyses of long bones have less uptake than
other parts of the bones, due to relatively low metabo
VetBooks.ir should, however, be smoothly homogenous with no
lism in the diaphyses of normal subjects. The uptake
focal areas of increased uptake. Contralateral imaging
can be useful when evaluating borderline lesions. Physes,
epiphyses, and apophyses demonstrate increased uptake
due to increased metabolic rates of bone tissue in these
regions.
Distal Limb (Foot, Pastern, and Fetlock)
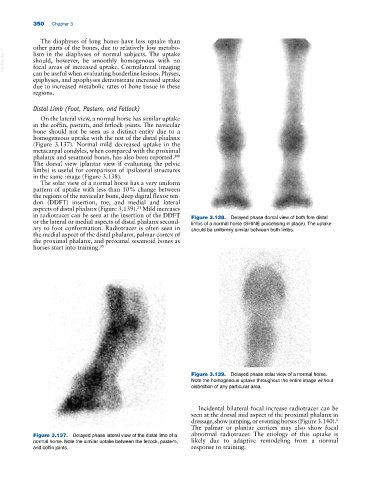
On the lateral view, a normal horse has similar uptake
in the coffin, pastern, and fetlock joints. The navicular
bone should not be seen as a distinct entity due to a
homogeneous uptake with the rest of the distal phalanx
(Figure 3.137). Normal mild decreased uptake in the
metacarpal condyles, when compared with the proximal
phalanx and sesamoid bones, has also been reported.
100
The dorsal view (plantar view if evaluating the pelvic
limbs) is useful for comparison of ipsilateral structures
in the same image (Figure 3.138).
The solar view of a normal horse has a very uniform
pattern of uptake with less than 10% change between
the regions of the navicular bone, deep digital flexor ten
don (DDFT) insertion, toe, and medial and lateral
aspects of distal phalanx (Figure 3.139). Mild increases
21
in radiotracer can be seen at the insertion of the DDFT Figure 3.138. Delayed phase dorsal view of both fore distal
or the lateral or medial aspects of distal phalanx second limbs of a normal horse (SHINE processing in place). The uptake
ary to foot conformation. Radiotracer is often seen in should be uniformly similar between both limbs.
the medial aspect of the distal phalanx, palmar cortex of
the proximal phalanx, and proximal sesamoid bones as
horses start into training. 35
Figure 3.139. Delayed phase solar view of a normal horse.
Note the homogenous uptake throughout the entire image without
distinction of any particular area.
Incidental bilateral focal increase radiotracer can be
seen at the dorsal mid aspect of the proximal phalanx in
dressage, show jumping, or eventing horses (Figure 3.140).
6
The palmar or plantar cortices may also show focal
Figure 3.137. Delayed phase lateral view of the distal limb of a abnormal radiotracer. The etiology of this uptake is
normal horse. Note the similar uptake between the fetlock, pastern, likely due to adaptive remodeling from a normal
and coffin joints. response to training.