Page 382 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 382
348 Chapter 3
part of the study most useful for evaluation of acute NORMAL BONE SCAN
lameness, e.g. incomplete or stress fractures in racehorses Vascular phase images are best viewed as a cine
VetBooks.ir also help in the diagnostic workup of horses presenting loop on the acquisition computer (a computer soft
or high‐performance horses. The delayed phase may
ware application that allows the images to be viewed
for other reasons such as ill‐defined lameness or lame
ness that is difficult to diagnose with regional anesthe sequentially in rapid order). A composite of vascular
sia, multiple causes of lameness in the same limb or phase images also can be generated, and it should
different regions of the body, acute lameness of unknown show good perfusion. When looking at the distal
origin, recheck of known lesion (to follow progress of limbs, try to have both limbs in a dorsal or palmar/
healing), evaluation of the physiologic activity of radio plantar view and look for perfusion symmetry.
graphic lesions, and evaluation of areas that are difficult Composite images of the distal aorta should show the
to radiograph such as the proximal thoracic and pelvic bifurcation of the aorta into the internal and external
limb, spine, and pelvis including the SI and coxofemoral iliac arteries (Figure 3.134).
joints. Delayed phase imaging is also useful for the Soft tissue (pool) phase images of the foot show some
assessment of bone viability and as a general survey in vascular activity, but the fetlock and pastern regions
prepurchase examinations. Soft tissue uptake in the should have homogeneously smooth uptake (Figure 3.135).
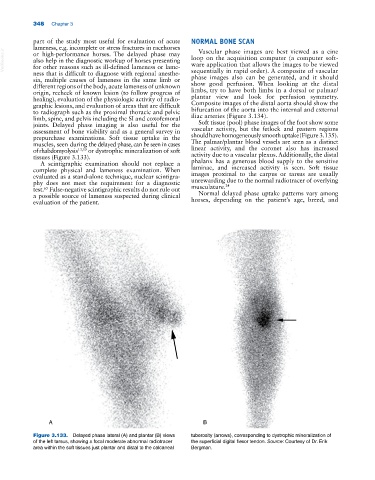
muscles, seen during the delayed phase, can be seen in cases The palmar/plantar blood vessels are seen as a distinct
of rhabdomyolysis 13,59 or dystrophic mineralization of soft linear activity, and the coronet also has increased
tissues (Figure 3.133). activity due to a vascular plexus. Additionally, the distal
A scintigraphic examination should not replace a phalanx has a generous blood supply to the sensitive
complete physical and lameness examination. When laminae, and increased activity is seen. Soft tissue
evaluated as a stand‐alone technique, nuclear scintigra images proximal to the carpus or tarsus are usually
phy does not meet the requirement for a diagnostic unrewarding due to the normal radiotracer of overlying
24
65
test. False‐negative scintigraphic results do not rule out musculature.
a possible source of lameness suspected during clinical Normal delayed phase uptake patterns vary among
evaluation of the patient. horses, depending on the patient’s age, breed, and
A B
Figure 3.133. Delayed phase lateral (A) and plantar (B) views tuberosity (arrows), corresponding to dystrophic mineralization of
of the left tarsus, showing a focal moderate abnormal radiotracer the superficial digital flexor tendon. Source: Courtesy of Dr. Erik
area within the soft tissues just plantar and distal to the calcaneal Bergman.