Page 453 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 453
Diagnostic Imaging 419
closer to and may contact the fourth metacarpal and irregular endosteal or periosteal contour due to new
metatarsal bones. bone formation (Figure 3.246). The palmar/plantar cor
VetBooks.ir Osseous Injury of the Third Metacarpal/Metatarsal Bone tive of trabecular bone resorption resulting in an altered
tex may further contain focal high intensity signal indica
contour with a focal concave bone defect.
The normal proximal palmar/plantar metacarpal/met Primary bone injuries without suspensory ligament
atarsal cortex has a uniform thickness and smooth peri abnormalities can also occur in the proximal palmar/
osteal and endosteal surfaces, although mild endosteal plantar aspect of the bone, with a similar range of MRI
and periosteal irregularity may be seen in some horses. abnormalities indicating fluid, sclerosis, or both. The
124
The smoothness of the palmar/plantar cortex at the ori exact cause of these bone injuries is unknown, but a
gin of the suspensory ligament is difficult to evaluate, mechanism of repetitive cortical fatigue or stress injury
because both the cortex and the suspensory ligament seems likely, 115,151 especially in horses that perform
have low signal intensity and cannot be distinguished strenuous exercise at high speed or over long distances,
from one another. Between 3 and 5 cm distal to the car even though the injury has been documented in many
pometacarpal joint, the metacarpal cortex is slightly different types and breeds. MRI signs of traumatic
115
thicker medially than laterally. bone bruising and remodeling appear predominantly on
Bone injury at the site of attachment of the suspensory the medial palmar aspect of the proximal portion of the
ligament not only occurs most frequently in combination metacarpus but not limited to the attachment area of
with proximal suspensory desmitis but also can be seen the suspensory ligament and have been described in
as an isolated injury. 5,28,93,127 Abnormalities indicative of young racing Thoroughbreds, 114,150 horses used for
enthesis bone injury at the origin of the suspensory liga endurance racing, and Western cutting horses. In a
29
5
ment include abnormal medullary signal hypointensity more advanced form of this traumatic fatigue injury,
on transverse PD and T2‐weighted images indicative of incomplete vertical or oblique hairline fractures of up to
increased bone density (sclerosis) (Figure 3.246), medul 9 cm length may develop in the proximopalmar medial
lary signal hyperintensity on STIR images and fat/water aspect of the third metacarpal bone. 82,114,115
cancelation artifact on T2* images compatible with the Isolated bone marrow lesions in the medullary cavity
presence of abnormal bone fluid, or a combination of of the third metacarpal/metatarsal bones can occur in
both sclerosis and fluid. Horses with chronic suspensory close relation to the nutrient foramen and intramedul
ligament lesions tend to have more sclerosis often with lary blood vessels as can focal enostosis‐like lesions.
thickening of the proximal palmar/plantar cortex and an
Figure 3.246. Transverse proton density image of the proximal
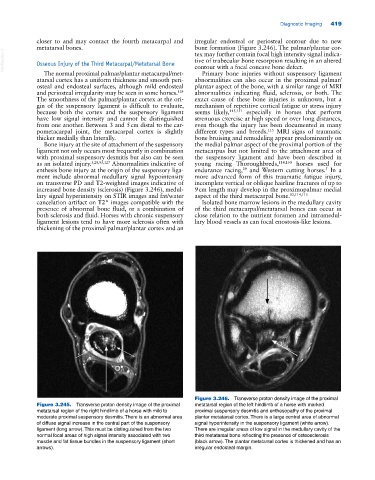
Figure 3.245. Transverse proton density image of the proximal metatarsal region of the left hindlimb of a horse with marked
metatarsal region of the right hindlimb of a horse with mild to proximal suspensory desmitis and enthesopathy of the proximal
moderate proximal suspensory desmitis. There is an abnormal area plantar metatarsal cortex. There is a large central area of abnormal
of diffuse signal increase in the central part of the suspensory signal hyperintensity in the suspensory ligament (white arrow).
ligament (long arrow). This must be distinguished from the two There are irregular areas of low signal in the medullary cavity of the
normal focal areas of high signal intensity associated with two third metatarsal bone reflecting the presence of osteosclerosis
muscle and fat tissue bundles in the suspensory ligament (short (black arrow). The plantar metatarsal cortex is thickened and has an
arrows). irregular endosteal margin.