Page 513 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 513
48 Gastrointestinal Imaging 481
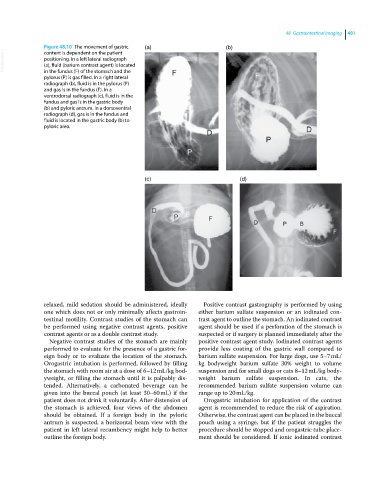
Figure 48.10 The movement of gastric (a) (b)
VetBooks.ir positioning. In a left lateral radiograph
content is dependent on the patient
(a), fluid (barium contrast agent) is located
in the fundus (F) of the stomach and the
pylorus (P) is gas filled. In a right lateral
radiograph (b), fluid is in the pylorus (P)
and gas is in the fundus (F). In a
ventrodorsal radiograph (c), fluid is in the
fundus and gas is in the gastric body
(b) and pyloric antrum. In a dorsoventral
radiograph (d), gas is in the fundus and
fluid is located in the gastric body (b) to
pyloric area.
(c) (d)
relaxed, mild sedation should be administered, ideally Positive contrast gastrography is performed by using
one which does not or only minimally affects gastroin either barium sulfate suspension or an iodinated con
testinal motility. Contrast studies of the stomach can trast agent to outline the stomach. An iodinated contrast
be performed using negative contrast agents, positive agent should be used if a perforation of the stomach is
contrast agents or as a double contrast study. suspected or if surgery is planned immediately after the
Negative contrast studies of the stomach are mainly positive contrast agent study. Iodinated contrast agents
performed to evaluate for the presence of a gastric for provide less coating of the gastric wall compared to
eign body or to evaluate the location of the stomach. barium sulfate suspension. For large dogs, use 5–7 mL/
Orogastric intubation is performed, followed by filling kg bodyweight barium sulfate 30% weight to volume
the stomach with room air at a dose of 6–12 mL/kg bod suspension and for small dogs or cats 8–12 mL/kg body
yweight, or filling the stomach until it is palpably dis weight barium sulfate suspension. In cats, the
tended. Alternatively, a carbonated beverage can be recommended barium sulfate suspension volume can
given into the buccal pouch (at least 30–60 mL) if the range up to 20 mL/kg.
patient does not drink it voluntarily. After distension of Orogastric intubation for application of the contrast
the stomach is achieved, four views of the abdomen agent is recommended to reduce the risk of aspiration.
should be obtained. If a foreign body in the pyloric Otherwise, the contrast agent can be placed in the buccal
antrum is suspected, a horizontal beam view with the pouch using a syringe, but if the patient struggles the
patient in left lateral recumbency might help to better procedure should be stopped and orogastric tube place
outline the foreign body. ment should be considered. If ionic iodinated contrast