Page 514 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 514
482 Section 6 Gastrointestinal Disease
(a) (b)
VetBooks.ir
(c) (d) (e)
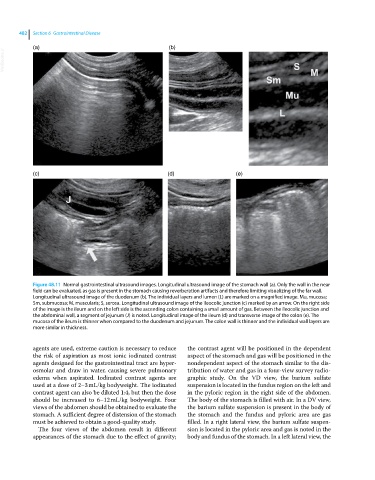
Figure 48.11 Normal gastrointestinal ultrasound images. Longitudinal ultrasound image of the stomach wall (a). Only the wall in the near
field can be evaluated, as gas is present in the stomach causing reverberation artifacts and therefore limiting visualizing of the far wall.
Longitudinal ultrasound image of the duodenum (b). The individual layers and lumen (L) are marked on a magnified image. Mu, mucosa;
Sm, submucosa; M, muscularis; S, serosa. Longitudinal ultrasound image of the ileocolic junction (c) marked by an arrow. On the right side
of the image is the ileum and on the left side is the ascending colon containing a small amount of gas. Between the ileocolic junction and
the abdominal wall, a segment of jejunum (J) is noted. Longitudinal image of the ileum (d) and transverse image of the colon (e). The
mucosa of the ileum is thinner when compared to the duodenum and jejunum. The colon wall is thinner and the individual wall layers are
more similar in thickness.
agents are used, extreme caution is necessary to reduce the contrast agent will be positioned in the dependent
the risk of aspiration as most ionic iodinated contrast aspect of the stomach and gas will be positioned in the
agents designed for the gastrointestinal tract are hyper nondependent aspect of the stomach similar to the dis
osmolar and draw in water, causing severe pulmonary tribution of water and gas in a four‐view survey radio
edema when aspirated. Iodinated contrast agents are graphic study. On the VD view, the barium sulfate
used at a dose of 2–3 mL/kg bodyweight. The iodinated suspension is located in the fundus region on the left and
contrast agent can also be diluted 1:4, but then the dose in the pyloric region in the right side of the abdomen.
should be increased to 6–12 mL/kg bodyweight. Four The body of the stomach is filled with air. In a DV view,
views of the abdomen should be obtained to evaluate the the barium sulfate suspension is present in the body of
stomach. A sufficient degree of distension of the stomach the stomach and the fundus and pyloric area are gas
must be achieved to obtain a good‐quality study. filled. In a right lateral view, the barium sulfate suspen
The four views of the abdomen result in different sion is located in the pyloric area and gas is noted in the
appearances of the stomach due to the effect of gravity; body and fundus of the stomach. In a left lateral view, the