Page 480 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 480
492 28 Reproduction
28.4 Radiography of the Male Cat The epididymis runs dorsally as a hypoechoic structure
along the testis, terminating at the coarsely hypoechoic
The prostate gland of the tom is not visible radiographi head and tail at either end. The vaginal tunics and tunica
cally. The feline prostate is approximately 1 cm in length albuginea present as a combined hyperechoic structure
and lies dorsally and laterally around the pelvic urethra [9]. seen peripherally. Anechoic tortuous vessels comprising
The location is similar to that of the male dog, 2–3 cm from the pampiniform plexus are located dorsal to the head of
the neck of the bladder. Problems affecting the prostate are the epididymis. The testicular parenchyma should be
infrequent in cats but have been reported. assessed for any irregularities including hypo‐ or hypere
choic areas, distinct masses, or areas of fibrosis. Each testi
cle should also be measured by obtaining the length, width,
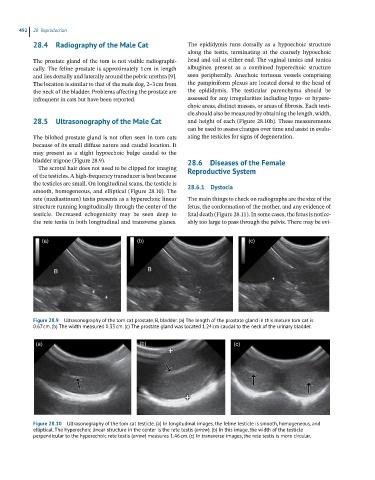
28.5 Ultrasonography of the Male Cat and height of each (Figure 28.10b). These measurements
can be used to assess changes over time and assist in evalu
The bilobed prostate gland is not often seen in tom cats ating the testicles for signs of degeneration.
because of its small diffuse nature and caudal location. It
may present as a slight hypoechoic bulge caudal to the
bladder trigone (Figure 28.9). 28.6 Diseases of the Female
The scrotal hair does not need to be clipped for imaging Reproductive System
of the testicles. A high‐frequency transducer is best because
the testicles are small. On longitudinal scans, the testicle is 28.6.1 Dystocia
smooth, homogeneous, and elliptical (Figure 28.10). The
rete (mediastinum) testis presents as a hyperechoic linear The main things to check on radiographs are the size of the
structure running longitudinally through the center of the fetus, the conformation of the mother, and any evidence of
testicle. Decreased echogenicity may be seen deep to fetal death (Figure 28.11). In some cases, the fetus is notice
the rete testis in both longitudinal and transverse planes. ably too large to pass through the pelvis. There may be evi
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 28.9 Ultrasonography of the tom cat prostate. B, bladder. (a) The length of the prostate gland in this mature tom cat is
0.67 cm. (b) The width measured 0.33 cm. (c) The prostate gland was located 1.24 cm caudal to the neck of the urinary bladder.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 28.10 Ultrasonography of the tom cat testicle. (a) In longitudinal images, the feline testicle is smooth, homogeneous, and
elliptical. The hyperechoic linear structure in the center is the rete testis (arrow). (b) In this image, the width of the testicle
perpendicular to the hyperechoic rete testis (arrow) measures 1.46 cm. (c) In transverse images, the rete testis is more circular.