Page 26 - GP Fall 2020
P. 26
Implant-supported Prostheses in Fixed Prosthodontics:
Design and Material Selection Criteria
By Siamak Najafi-Abrandabadi, DDS and Peerapol Tevavichulada, DDS
Introduction margin should not be deeper than 1mm. • Hybrid Abutments
Dental implants are sometimes the best This design requires at least 6mm of inter- Hybrid abutment designs consist of a tita-
option to replace missing teeth. Prosthetic occlusal space. 1,2 nium insert and an all-ceramic customized
parts of implant restorations consist of the abutment that can be bonded to the insert.
abutment and the crown. There are multi- Abutment Materials (Figure 4) They have a titanium connection
ple materials and different ways to design There are various materials that can be used
the implant-supported restorations. Titani- to fabricate implant abutments. Clinicians
um abutments and porcelain-fused-to-metal should understand the properties and bio-
crowns have been popular designs for clini- logic response of each material. The most
cians and have been used for decades. How- commonly used implant abutment materials
ever, this design has potential complications are titanium, metal alloy, hybrid, and all-ce-
such as gingival discoloration and metal ramic, such as alumina and zirconia.
show-through that effect esthetic results,
especially in anterior teeth. The purpose of • Titanium Abutments
this article is to review selection criteria in Titanium is usually used to fabricate abut-
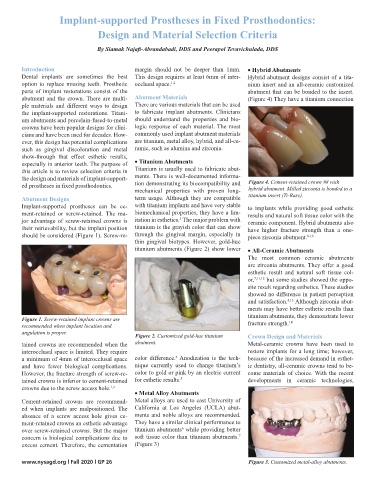
the design and materials of implant-support- ments. There is well-documented informa- Figure 4. Cement-retained crown #8 with
ed prostheses in fixed prosthodontics. tion demonstrating its biocompatibility and hybrid abutment. Milled zirconia is bonded to a
mechanical properties with proven long-
Abutment Designs term usage. Although they are compatible titanium insert (Ti-Base).
Implant-supported prostheses can be ce- with titanium implants and have very stable to implants while providing good esthetic
ment-retained or screw-retained. The ma- biomechanical properties, they have a lim- results and natural soft tissue color with the
jor advantage of screw-retained crowns is itation in esthetics. The major problem with ceramic component. Hybrid abutments also
3
their retrievability, but the implant position titanium is the grayish color that can show have higher fracture strength than a one-
should be considered (Figure 1). Screw-re- through the gingival margin, especially in piece zirconia abutment. 8-10
thin gingival biotypes. However, gold-hue
titanium abutments (Figure 2) show lower • All-Ceramic Abutments
The most common ceramic abutments
are zirconia abutments. They offer a good
esthetic result and natural soft tissue col-
or, 7,11,12 but some studies showed the oppo-
site result regarding esthetics. These studies
showed no difference in patient perception
and satisfaction. 4,13 Although zirconia abut-
ments may have better esthetic results than
Figure 1. Screw-retained implant crowns are titanium abutments, they demonstrate lower
14
recommended when implant location and fracture strength.
angulation is proper.
Figure 2. Customized gold-hue titanium Crown Design and Materials
tained crowns are recommended when the abutment. Metal-ceramic crowns have been used to
interocclusal space is limited. They require restore implants for a long time; however,
a minimum of 4mm of interocclusal space color difference. Anodization is the tech- because of the increased demand in esthet-
4
and have fewer biological complications. nique currently used to change titanium’s ic dentistry, all-ceramic crowns tend to be-
However, the fracture strength of screw-re- color to gold or pink by an electric current come materials of choice. With the recent
tained crowns is inferior to cement-retained for esthetic results. 5 developments in ceramic technologies,
crowns due to the screw access hole. 1,2
• Metal Alloy Abutments
Cement-retained crowns are recommend- Metal alloys are used to cast University of
ed when implants are malpositioned. The California at Los Angeles (UCLA) abut-
absence of a screw access hole gives ce- ments and noble alloys are recommended.
ment-retained crowns an esthetic advantage They have a similar clinical performance to
over screw-retained crowns. But the major titanium abutments while providing better
6
concern is biological complications due to soft tissue color than titanium abutments.
7
excess cement. Therefore, the cementation (Figure 3)
www.nysagd.org l Fall 2020 l GP 26 Figure 3. Customized metal-alloy abutments.