Page 253 - Essential Haematology
P. 253
Chapter 18 Chronic lymphoid leukaemias / 239
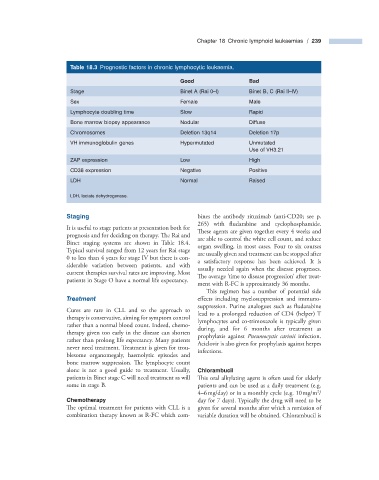
Table 18.3 Prognostic factors in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Good Bad
Stage Binet A (Rai 0 – I) Binet B, C (Rai II – IV)
Sex Female Male
Lymphocyte doubling time Slow Rapid
Bone marrow biopsy appearance Nodular Diffuse
Chromosomes Deletion 13q14 Deletion 17p
VH immunoglobulin genes Hypermutated Unmutated
Use of VH3.21
ZAP expression Low High
CD38 expression Negative Positive
LDH Normal Raised
LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.
Staging bines the antibody rituximab (anti - CD20; see p.
265 ) with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide.
It is useful to stage patients at presentation both for
These agents are given together every 4 weeks and
prognosis and for deciding on therapy. The Rai and
are able to control the white cell count, and reduce
Binet staging systems are shown in Table 18.4 .
organ swelling, in most cases. Four to six courses
Typical survival ranged from 12 years for Rai stage
are usually given and treatment can be stopped after
0 to less than 4 years for stage IV but there is con-
a satisfactory response has been achieved. It is
siderable variation between patients, and with
usually needed again when the disease progresses.
current therapies survival rates are improving. Most
The average time to disease progression ’ after treat-
‘
patients in Stage O have a normal life expectancy.
ment with R - FC is approximately 36 months.
This regimen has a number of potential side
Treatment effects including myelosuppression and immuno-
suppression. Purine analogues such as fl udarabine
Cures are rare in CLL and so the approach to
lead to a prolonged reduction of CD4 (helper) T
therapy is conservative, aiming for symptom control
lymphocytes and co - trimoxazole is typically given
rather than a normal blood count. Indeed, chemo-
during, and for 6 months after treatment as
therapy given too early in the disease can shorten
prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii infection.
rather than prolong life expectancy. Many patients
Aciclovir is also given for prophylaxis against herpes
never need treatment. Treatment is given for trou-
infections.
blesome organomegaly, haemolytic episodes and
bone marrow suppression. The lymphocyte count
alone is not a good guide to treatment. Usually, Chlorambucil
patients in Binet stage C will need treatment as will Th is oral alkylating agent is often used for elderly
some in stage B. patients and can be used as a daily treatment (e.g.
2
4 – 6 mg/day) or in a monthly cycle (e.g. 10 mg/m /
Chemotherapy day for 7 days). Typically the drug will need to be
The optimal treatment for patients with CLL is a given for several months after which a remission of
combination therapy known as R - FC which com- variable duration will be obtained. Chlorambucil is