Page 257 - Essential Haematology
P. 257
Chapter 18 Chronic lymphoid leukaemias / 243
(a) (b)
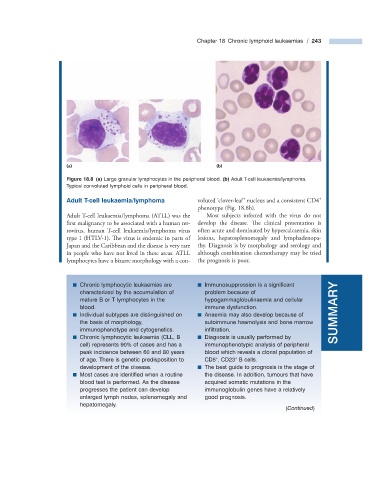
Figure 18.8 (a) Large granular lymphocytes in the peripheral blood. (b) Adult T - cell leukaemia/lymphoma.
Typical convoluted lymphoid cells in peripheral blood.
+
Adult T - c ell l eukaemia/lymphoma voluted ‘ clover - leaf ’ nucleus and a consistent CD4
phenotype (Fig. 18.8 b).
Adult T - cell leukaemia/lymphoma (ATLL) was the Most subjects infected with the virus do not
first malignancy to be associated with a human ret- develop the disease. The clinical presentation is
rovirus, human T - cell leukaemia/lymphoma virus often acute and dominated by hypercalcaemia, skin
type 1 (HTLV - 1). The virus is endemic in parts of lesions, hepatosplenomegaly and lymphadenopa-
Japan and the Caribbean and the disease is very rare thy. Diagnosis is by morphology and serology and
in people who have not lived in these areas. ATLL although combination chemotherapy may be tried
lymphocytes have a bizarre morphology with a con- the prognosis is poor.
■ Chronic lymphocytic leukaemias are ■ Immunosuppression is a signifi cant
characterized by the accumulation of problem because of
mature B or T lymphocytes in the hypogammaglobulinaemia and cellular
blood. immune dysfunction.
■ Individual subtypes are distinguished on ■ Anaemia may also develop because of SUMMARY
the basis of morphology, autoimmune haemolysis and bone marrow
immunophenotype and cytogenetics. infi ltration.
■ Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL, B ■ Diagnosis is usually performed by
cell) represents 90% of cases and has a immunophenotypic analysis of peripheral
peak incidence between 60 and 80 years blood which reveals a clonal population of
+
+
of age. There is genetic predisposition to CD5 , CD23 B cells.
development of the disease. ■ The best guide to prognosis is the stage of
■ Most cases are identifi ed when a routine the disease. In addition, tumours that have
blood test is performed. As the disease acquired somatic mutations in the
progresses the patient can develop immunoglobulin genes have a relatively
enlarged lymph nodes, splenomegaly and good prognosis.
hepatomegaly.
(Continued)