Page 32 - Essential Haematology
P. 32
18 / Chapter 2 Erythropoiesis and anaemia
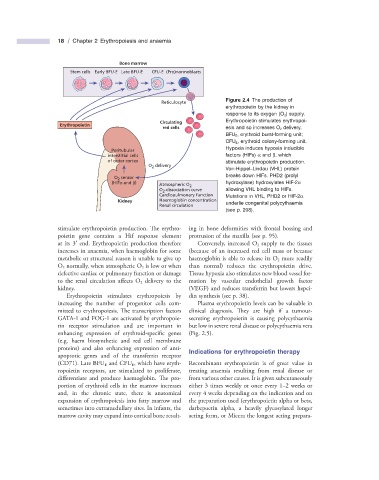
Bone marrow
Stem cells Early BFU-E Late BFU-E CFU-E (Pro)normoblasts
Figure 2.4 The production of
Reticulocyte
erythropoietin by the kidney in
response to its oxygen (O 2 ) supply.
Circulating Erythropoietin stimulates erythropoi-
Erythropoietin
red cells esis and so increases O 2 delivery.
BFU E , erythroid burst - forming unit;
CFU E , erythroid colony - forming unit.
Hypoxia induces hypoxia inducible
Peritubular
interstitial cells factors (HIFs) α and β , which
of outer cortex stimulate erythropoietin production.
O delivery
2
Von - Hippel – Lindau (VHL) protein
O 2 sensor breaks down HIFs. PHD2 (prolyl
(HIFα and β) hydroxylase) hydroxylates HIF - 2 α
Atmospheric O 2
O -dissociation curve allowing VHL binding to HIFs.
2
Cardiopulmonary function Mutations in VHL, PHD2 or HIF - 2 α
Kidney Haemoglobin concentration underlie congenital polycythaemia
Renal circulation
(see p. 208).
stimulate erythropoietin production. Th e erythro- ing in bone deformities with frontal bossing and
poietin gene contains a Hif response element protrusion of the maxilla (see p. 95 ).
′
at its 3 end. Erythropoietin production therefore Conversely, increased O 2 supply to the tissues
increases in anaemia, when haemoglobin for some (because of an increased red cell mass or because
metabolic or structural reason is unable to give up haemoglobin is able to release its O 2 more readily
O 2 normally, when atmospheric O 2 is low or when than normal) reduces the erythropoietin drive.
defective cardiac or pulmonary function or damage Tissue hypoxia also stimulates new blood vessel for-
to the renal circulation aff ects O 2 delivery to the mation by vascular endothelial growth factor
kidney. (VEGF) and reduces transferrin but lowers hepci-
Erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis by din synthesis (see p. 38 ).
increasing the number of progenitor cells com- Plasma erythropoietin levels can be valuable in
mitted to erythropoiesis. The transcription factors clinical diagnosis. They are high if a tumour -
GATA - 1 and FOG - 1 are activated by erythropoie- secreting erythropoietin is causing polycythaemia
tin receptor stimulation and are important in but low in severe renal disease or polycythaemia vera
enhancing expression of erythroid - specifi c genes (Fig. 2.5 ).
(e.g. haem biosynthetic and red cell membrane
proteins) and also enhancing expression of anti -
Indications for e rythropoietin t herapy
apoptotic genes and of the transferrin receptor
(CD71). Late BFU E and CFU E , which have eryth- Recombinant erythropoietin is of great value in
ropoietin receptors, are stimulated to proliferate, treating anaemia resulting from renal disease or
differentiate and produce haemoglobin. Th e pro- from various other causes. It is given subcutaneously
portion of erythroid cells in the marrow increases either 3 times weekly or once every 1 – 2 weeks or
and, in the chronic state, there is anatomical every 4 weeks depending on the indication and on
expansion of erythropoiesis into fatty marrow and the preparation used (erythropoietin alpha or beta,
sometimes into extramedullary sites. In infants, the darbepoetin alpha, a heavily glycosylated longer
marrow cavity may expand into cortical bone result- acting form, or Micera the longest acting prepara-