Page 33 - Essential Haematology
P. 33
Chapter 2 Erythropoiesis and anaemia / 19
10 5 Table 2.1 Clinical uses of erythropoietin.
Normal
Anaemias Anaemia of chronic renal disease
Renal failure:
Nephric Myelodysplastic syndrome
Anephric
Anaemia associated with malignancy and
10 4 chemotherapy
Anaemia of chronic diseases, e.g. rheumatoid
arthritis
EPO (mIU/mL) 10 3 Perioperative uses
Anaemia of prematurity
Table 2.2 Normal haemoglobins in adult
blood.
10 2
Hb A Hb F Hb A 2
Structure α 2 2 α 2 2 α 2 2
β
δ
γ
Normal (%) 96 – 98 0.5 – 0.8 1.5 – 3.2
10 1
4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
Haemoglobin (g/dL)
folate, vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B 6 , thiamine
and riboflavin) and hormones such as androgens
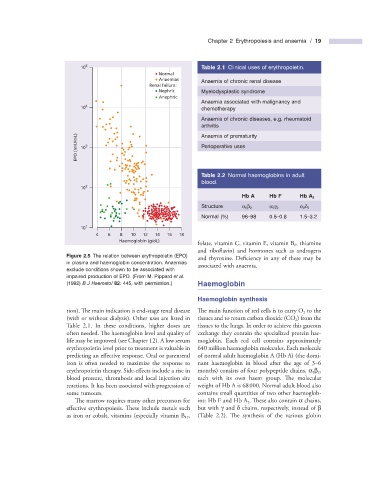
Figure 2.5 The relation between erythropoietin (EPO)
and thyroxine. Deficiency in any of these may be
in plasma and haemoglobin concentration. Anaemias
associated with anaemia.
exclude conditions shown to be associated with
impaired production of EPO. (From M. Pippard et al .
(1992) B J Haematol 82 : 445, with permission.) Haemoglobin
Haemoglobin s ynthesis
tion). The main indication is end - stage renal disease The main function of red cells is to carry O 2 to the
(with or without dialysis). Other uses are listed in tissues and to return carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) from the
Table 2.1 . In these conditions, higher doses are tissues to the lungs. In order to achieve this gaseous
often needed. The haemoglobin level and quality of exchange they contain the specialized protein hae-
life may be improved (see Chapter 12 ). A low serum moglobin. Each red cell contains approximately
erythropoietin level prior to treatment is valuable in 640 million haemoglobin molecules. Each molecule
predicting an effective response. Oral or parenteral of normal adult haemoglobin A (Hb A) (the domi-
iron is often needed to maximize the response to nant haemoglobin in blood after the age of 3 – 6
erythropoietin therapy. Side - effects include a rise in months) consists of four polypeptide chains, α 2 β 2 ,
blood pressure, thrombosis and local injection site each with its own haem group. Th e molecular
reactions. It has been associated with progression of weight of Hb A is 68 000. Normal adult blood also
some tumours. contains small quantities of two other haemoglob-
The marrow requires many other precursors for ins: Hb F and Hb A 2 . These also contain α chains,
effective erythropoiesis. These include metals such but with γ and δ chains, respectively, instead of β
as iron or cobalt, vitamins (especially vitamin B 12 , (Table 2.2 ). The synthesis of the various globin