Page 73 - Essential Haematology
P. 73
Chapter 5 Macrocytic anaemias / 59
Introduction to m acrocytic taminated foods. The vitamin consists of a small
group of compounds, the cobalamins, which have
a naemia
the same basic structure, with a cobalt atom at the
In macrocytic anaemia the red cells are abnormally centre of a corrin ring which is attached to a nucle-
large (mean corpuscular volume, MCV > 98 fL). otide portion (Fig. 5.1 ). The vitamin is found in
There are several causes (see Table 2.4 ) but they can foods of animal origin such as liver, meat, fi sh and
be broadly subdivided into megaloblastic and non - dairy produce but does not occur in fruit, cereals or
megaloblastic (Table 5.10 ), based on the appearance vegetables. Table 5.2 compares nutritional aspects
of developing erythroblasts in the bone marrow. of B 12 and folate.
Megaloblastic a naemias Absorption
This is a group of anaemias in which the erythro- A normal diet contains a large excess of B 12 com-
blasts in the bone marrow show a characteristic pared with daily needs (Table 5.2 ). B 12 is released
abnormality – maturation of the nucleus being from protein - binding in food and is combined with
delayed relative to that of the cytoplasm. Th e under- the glycoprotein intrinsic factor (IF) (molecular
lying defect accounting for the asynchronous matu- weight 45 000) which is synthesized by the gastric
ration of the nucleus is defective DNA synthesis and parietal cells. The IF – B 12 complex can then bind to
this is usually caused by deficiency of vitamin B 12 a specific surface receptor for IF, cubilin, which then
or folate. Less commonly, abnormalities of metabo- binds to a second protein, amnionless, which directs
lism of these vitamins or other lesions in DNA endocytosis of the cubilin IF – B 12 complex in the
synthesis may cause an identical haematological
appearance (Table 5.1 ).
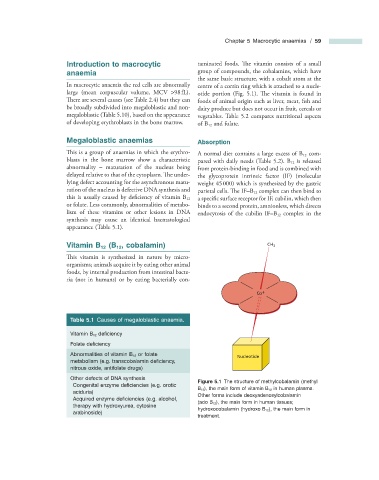
Vitamin B 12 ( B 12 , c obalamin) CH 3
This vitamin is synthesized in nature by micro-
organisms; animals acquire it by eating other animal
foods, by internal production from intestinal bacte-
ria (not in humans) or by eating bacterially con-
Co +
Table 5.1 Causes of megaloblastic anaemia.
Vitamin B 12 defi ciency
Folate defi ciency
Abnormalities of vitamin B 12 or folate Nucleotide
metabolism (e.g. transcobalamin defi ciency,
nitrous oxide, antifolate drugs)
Other defects of DNA synthesis
Figure 5.1 The structure of methylcobalamin (methyl
Congenital enzyme defi ciencies (e.g. orotic
B 12 ), the main form of vitamin B 12 in human plasma.
aciduria)
Other forms include deoxyadenosylcobalamin
Acquired enzyme defi ciencies (e.g. alcohol,
(ado B 12 ), the main form in human tissues;
therapy with hydroxyurea, cytosine
hydroxocobalamin (hydroxo B 12 ), the main form in
arabinoside)
treatment.