Page 68 - Essential Haematology
P. 68
54 / Chapter 4 Iron overload
(a) (b)
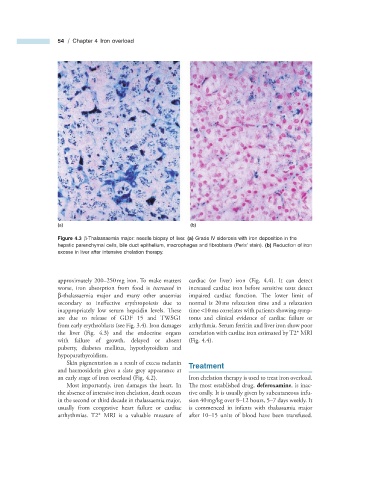
Figure 4.3 β - Thalassaemia major: needle biopsy of liver. (a) Grade IV siderosis with iron deposition in the
hepatic parenchymal cells, bile duct epithelium, macrophages and fi broblasts (Perls ’ stain). (b) Reduction of iron
excess in liver after intensive chelation therapy.
approximately 200 – 250 mg iron. To make matters cardiac (or liver) iron (Fig. 4.4 ). It can detect
worse, iron absorption from food is increased in increased cardiac iron before sensitive tests detect
β - thalassaemia major and many other anaemias impaired cardiac function. The lower limit of
secondary to ineffective erythropoiesis due to normal is 20 ms relaxation time and a relaxation
inappropriately low serum hepcidin levels. Th ese time < 10 ms correlates with patients showing symp-
are due to release of GDF 15 and TWSG1 toms and clinical evidence of cardiac failure or
from early erythroblasts (see Fig. 3.4 ). Iron damages arrhythmia. Serum ferritin and liver iron show poor
the liver (Fig. 4.3 ) and the endocrine organs correlation with cardiac iron estimated by T2 * MRI
with failure of growth, delayed or absent (Fig. 4.4 ).
puberty, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and
hypoparathyroidism.
Skin pigmentation as a result of excess melanin Treatment
and haemosiderin gives a slate grey appearance at
an early stage of iron overload (Fig. 4.2 ). Iron chelation therapy is used to treat iron overload.
Most importantly, iron damages the heart. In The most established drug, deferoxamine , is inac-
the absence of intensive iron chelation, death occurs tive orally. It is usually given by subcutaneous infu-
in the second or third decade in thalassaemia major, sion 40 mg/kg over 8 – 12 hours, 5 – 7 days weekly. It
usually from congestive heart failure or cardiac is commenced in infants with thalassamia major
arrhythmias. T2 * MRI is a valuable measure of after 10 – 15 units of blood have been transfused.