Page 642 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 642
(insulin-secreting) cells through local action within the pancreatic islets. It
also inhibits the production of bicarbonate and enzymes by the exocrine cells
of the pancreas.
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells produce the hormone pancreatic
polypeptide. This hormone inhibits the production of bile and intestinal
motility, inhibits pancreatic enzymes and bicarbonate secretions, and
stimulates the gastric chief (zymogen) cells.
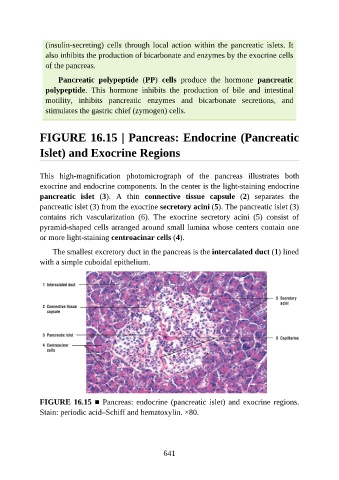
FIGURE 16.15 | Pancreas: Endocrine (Pancreatic
Islet) and Exocrine Regions
This high-magnification photomicrograph of the pancreas illustrates both
exocrine and endocrine components. In the center is the light-staining endocrine
pancreatic islet (3). A thin connective tissue capsule (2) separates the
pancreatic islet (3) from the exocrine secretory acini (5). The pancreatic islet (3)
contains rich vascularization (6). The exocrine secretory acini (5) consist of
pyramid-shaped cells arranged around small lumina whose centers contain one
or more light-staining centroacinar cells (4).
The smallest excretory duct in the pancreas is the intercalated duct (1) lined
with a simple cuboidal epithelium.
FIGURE 16.15 ■ Pancreas: endocrine (pancreatic islet) and exocrine regions.
Stain: periodic acid–Schiff and hematoxylin. ×80.
641