Page 894 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 894
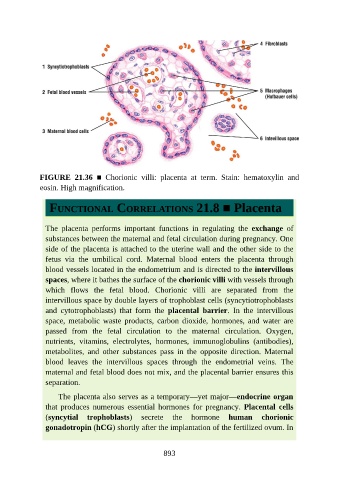
FIGURE 21.36 ■ Chorionic villi: placenta at term. Stain: hematoxylin and
eosin. High magnification.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 21.8 ■ Placenta
The placenta performs important functions in regulating the exchange of
substances between the maternal and fetal circulation during pregnancy. One
side of the placenta is attached to the uterine wall and the other side to the
fetus via the umbilical cord. Maternal blood enters the placenta through
blood vessels located in the endometrium and is directed to the intervillous
spaces, where it bathes the surface of the chorionic villi with vessels through
which flows the fetal blood. Chorionic villi are separated from the
intervillous space by double layers of trophoblast cells (syncytiotrophoblasts
and cytotrophoblasts) that form the placental barrier. In the intervillous
space, metabolic waste products, carbon dioxide, hormones, and water are
passed from the fetal circulation to the maternal circulation. Oxygen,
nutrients, vitamins, electrolytes, hormones, immunoglobulins (antibodies),
metabolites, and other substances pass in the opposite direction. Maternal
blood leaves the intervillous spaces through the endometrial veins. The
maternal and fetal blood does not mix, and the placental barrier ensures this
separation.
The placenta also serves as a temporary—yet major—endocrine organ
that produces numerous essential hormones for pregnancy. Placental cells
(syncytial trophoblasts) secrete the hormone human chorionic
gonadotropin (hCG) shortly after the implantation of the fertilized ovum. In
893