Page 19 - Shroeder - Filter Systems
P. 19
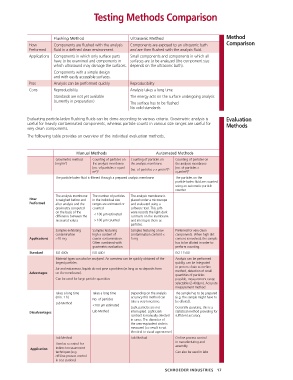
Testing Methods Comparison
Flushing Method Ultrasonic Method Method
How Components are flushed with the analysis Components are exposed to an ultrasonic bath Comparison
Preformed fluid in a defined clean environment. and are then flushed with the analysis fluid.
Applications Components in which only surface parts Small components and components in which all
have to be examined and components in surfaces are to be analyzed (the component size
which ultrasound may damage the surfaces. depends on the ultrasonic bath).
Components with a simple design
and with easily accessible surfaces.
Pros Analysis can be performed quickly Reproducibility
Cons Reproducibility Analysis takes a long time
Standards are not yet available The energy acts on the surface undergoing analysis
(currently in preparation) The surface has to be flushed
No valid standards
Evaluating particle-laden flushing fluids can be done according to various criteria. Gravimetric analysis is Evaluation
useful for heavily contaminated components, whereas particle counts in various size ranges are useful for Methods
very clean components.
The following table provides an overview of the individual evaluation methods.
Manual Methods Automated Methods
Gravimetric method Counting of particles on Counting of particles on Counting of particles on
[mg/m 2 ] the analysis membrane the analysis membrane the analysis membrane
[no. of particles > x µm/ [no. of particles > x µm/m 2 ]* [no. of particles >
m 2 ]* x µm/m 2 ]*
The particle-laden fluid is filtered through a prepared analysis membrane The particles on the
particle-laden fluid are counted
using an automatic particle
counter
The analysis membrane The number of particles The analysis membrane is
How is weighed before and in the individual size placed under a microscope
Performed after analysis and the ranges are estimated or and evaluated using a
gravimetry computed counted software tool. This soft-
on the basis of the < 100 µm estimated ware records the light-dark
difference between the contrasts on the membrane
measured values > 100 µm counted and interrupts them as
particles.
Samples exhibiting Samples featuring Samples featuring a low Preferred for very clean
contamination high a content of contamination content < components. When high dirt
Applications >10 mg coarse contamination. 5 mg content is involved, the sample
Often combined with has to be diluted in order to
gravimetric evaluation. perform counting.
Standard ISO 4405 ISO 4407 ISO 11500
Material types can also be analyzed. An overview can be quickly obtained of the Analysis can be performed
largest particles. quickly, can be integrated
in process chain as on-line
Air and extraneous liquids do not pose a problem (as long as no deposits form
Advantages on the membrane). method, detection of small
quantities of particles
Can be used for large particle quantities possible, measurement range
selectable (2-400µm). Accurate
measurement method
Takes a long time Takes a long time Depending on the analysis The sample has to be prepared
(min. 1 h) accuracy this method can (e.g. the sample might have to
No. of particles
Lab Method take a very long time. be diluted).
<100 µm estimated
Light particles are not Generally speaking, this is a
Disadvantages Lab Method interrupted. Light-Dark statistical method providing for
contrast is manually selected sufficient accuracy.
in cases. The diameter of
the area-equivalent circle is
measured (=> result is not
identical to visual appearance)
Lab Method Lab Method On-line process control
in manufacturing and
Used as a control for assembly.
Application indirect measurement
techniques (e.g. Can also be used in labs
off-line process control
in test stations)
SCHROEDER INDUSTRIES 17