Page 21 - mathematics
P. 21
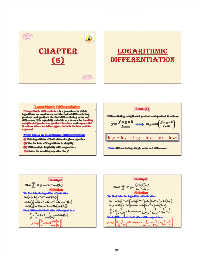
Logarithmic Differentiation Case (1)
* Logarithmic differentiation is a procedure in which Differentiating complicated product and quotient functions:
logarithms are used to convert the task of differentiating
products and quotients for that differentiating sums and y f gh ln y ln f gh
differences. It is especially valuable as a means for handling lm lm
complicated product or quotient functions and exponential
functions where variables appear in both the base and the ln y ln f ln g ln h ln l ln m
exponent.
Now: differentiating simple sums and differences.
Main Steps in logarithmic Differentiation:
(i) Take logarithms of both sides of a given equation
(ii) Use the laws of Logarithms to simplify.
(iii) Differentiate implicitly with respect to x.
(iv) Solve the resulting equation for y'.
Example Example
dy x 2 1 e5 sin x
dx if y tan1 x ln x
Find if y x3 e2x cos(3x) Find dy
dx
Solution
Solution
We first take the logarithm of both sides:
ln y ln x 3 e 2x cos3 (3x ) We first take the logarithm of both sides:
ln y ln x3 ln e2x ln cos3 3x ln y ln x 2 1 5 ln e sin x ln tan1 x ln ln x
ln y 5ln x 2 1 sin x ln tan1 x ln ln x
ln y 3ln x 2 x 3ln cos3x
Next, differentiate both sides with respect to x: y 51 2x cos x 1 1 2 1 1
x 2 1 tan1 x 1 x ln x x
y 3 2 3 1 3 sin 3 x y
y x Next, differentiate both sides with respect to x:
cos 3 x
3 sin 3x 5 1 cos x 1 1 1 1
x cos 3x x 2 1 tan 1 1 x ln x x
y y 2 9 y y 2x x 2
21