Page 22 - mathematics
P. 22
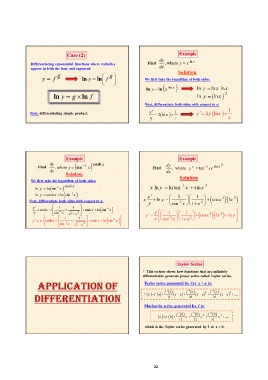
Case (2) Example
Differentiating exponential functions where variables Find dy , where y x ln x
dx
appear in both the base and exponent:
Solution
y fg ln y ln f g
We first take the logarithm of both sides:
ln y g ln f ln y ln x ln x ln y ln x ln x
ln y ln x 2
Next, differentiate both sides with respect to x:
Now: differentiating simple product. y 2 ln x 1 y 2 y ln x 1
y x x
Example Example
Find dy cosh x dy y x tan1 xe sinx 3
dx , where y sin 1 x Find dx , where
Solution Solution
We first take the logarithm of both sides: x ln y ln tan1 x sin x 3
ln y ln sin1 x cosh x xy 1 1 3x 2
y ln y tan1 1 x cos x 3
ln y cosh x ln sin1 x
Next, differentiate both sides with respect to x: x 2
y 1 1
sin 1
y
cosh x x 2 sinh x ln sin1 x y 1 1
x tan1 x x
1 x y
cosh x 2 cos x 3 3x 2 ln y
1 1 1
y y sin 1 1x 2
x sinh x ln sin1 x
Taylor Series
* This section shows how functions that are infinitely
differentiable generate power series called Taylor series.
Taylor series generated by f at x = a is:
f x f a f a x a f a x a2 f a x a 3 ....
1! 2! 3!
Maclaurin series generated by f is:
f x f 0 f 0 x f 0 x 2 f 0 x 3 ....
1! 2! 3!
which is the Taylor series generated by f at x = 0.
22