Page 96 - Analytical Chemistry I E-book
P. 96
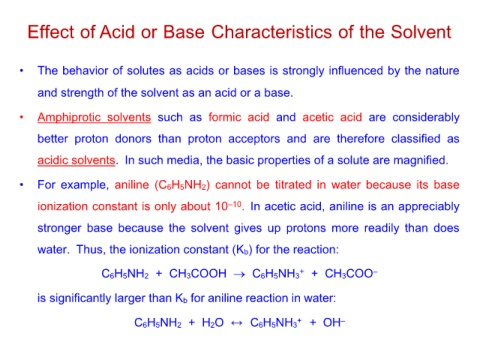
Effect of Acid or Base Characteristics of the Solvent
• The behavior of solutes as acids or bases is strongly influenced by the nature
and strength of the solvent as an acid or a base.
• Amphiprotic solvents such as formic acid and acetic acid are considerably
better proton donors than proton acceptors and are therefore classified as
acidic solvents. In such media, the basic properties of a solute are magnified.
• For example, aniline (C6H5NH2) cannot be titrated in water because its base
ionization constant is only about 10–10. In acetic acid, aniline is an appreciably
stronger base because the solvent gives up protons more readily than does
water. Thus, the ionization constant (Kb) for the reaction:
C6H5NH2 + CH3COOH → C6H5NH3+ + CH3COO–
is significantly larger than Kb for aniline reaction in water:
C6H5NH2 + H2O C6H5NH3+ + OH–