Page 22 - May
P. 22
METALWORKING EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS
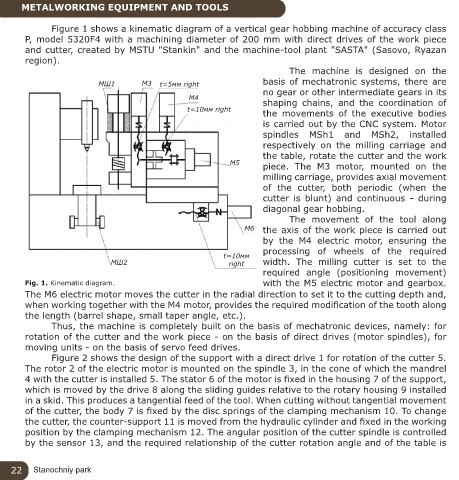
Figure 1 shows a kinematic diagram of a vertical gear hobbing machine of accuracy class
P, model 5320F4 with a machining diameter of 200 mm with direct drives of the work piece
and cutter, created by MSTU "Stankin" and the machine-tool plant "SASTA" (Sasovo, Ryazan
region).
The machine is designed on the
МШ1 М3 t=5мм right basis of mechatronic systems, there are
no gear or other intermediate gears in its
М4 shaping chains, and the coordination of
t=10мм right the movements of the executive bodies
is carried out by the CNC system. Motor
spindles MSh1 and MSh2, installed
respectively on the milling carriage and
the table, rotate the cutter and the work
М5 piece. The M3 motor, mounted on the
milling carriage, provides axial movement
of the cutter, both periodic (when the
cutter is blunt) and continuous - during
diagonal gear hobbing.
The movement of the tool along
М6 the axis of the work piece is carried out
by the M4 electric motor, ensuring the
processing of wheels of the required
t=10мм
МШ2 right width. The milling cutter is set to the
required angle (positioning movement)
Fig. 1. Kinematic diagram. with the M5 electric motor and gearbox.
The M6 electric motor moves the cutter in the radial direction to set it to the cutting depth and,
when working together with the M4 motor, provides the required modification of the tooth along
the length (barrel shape, small taper angle, etc.).
Thus, the machine is completely built on the basis of mechatronic devices, namely: for
rotation of the cutter and the work piece - on the basis of direct drives (motor spindles), for
moving units - on the basis of servo feed drives.
Figure 2 shows the design of the support with a direct drive 1 for rotation of the cutter 5.
The rotor 2 of the electric motor is mounted on the spindle 3, in the cone of which the mandrel
4 with the cutter is installed 5. The stator 6 of the motor is fixed in the housing 7 of the support,
which is moved by the drive 8 along the sliding guides relative to the rotary housing 9 installed
in a skid. This produces a tangential feed of the tool. When cutting without tangential movement
of the cutter, the body 7 is fixed by the disc springs of the clamping mechanism 10. To change
the cutter, the counter-support 11 is moved from the hydraulic cylinder and fixed in the working
position by the clamping mechanism 12. The angular position of the cutter spindle is controlled
by the sensor 13, and the required relationship of the cutter rotation angle and of the table is
22 Stanochniy park