Page 526 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 526
516 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
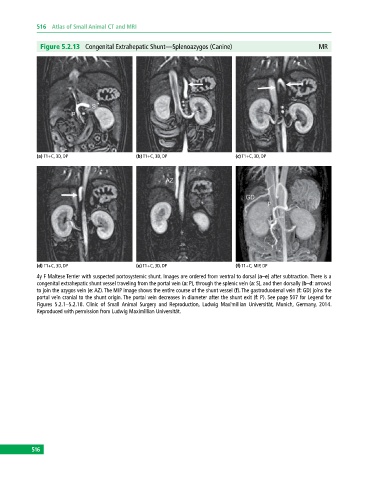
Figure 5.2.13 Congenital Extrahepatic Shunt—Splenoazygos (Canine) MR
(a) T1+C, 3D, DP (b) T1+C, 3D, DP (c) T1+C, 3D, DP
(d) T1+C, 3D, DP (e) T1+C, 3D, DP (f) T1+C, MIP, DP
4y F Maltese Terrier with suspected portosystemic shunt. Images are ordered from ventral to dorsal (a–e) after subtraction. There is a
congenital extrahepatic shunt vessel traveling from the portal vein (a: P), through the splenic vein (a: S), and then dorsally (b–d: arrows)
to join the azygos vein (e: AZ). The MIP image shows the entire course of the shunt vessel (f). The gastroduodenal vein (f: GD) joins the
portal vein cranial to the shunt origin. The portal vein decreases in diameter after the shunt exit (f: P). See page 507 for Legend for
Figures 5.2.1–5.2.18. Clinic of Small Animal Surgery and Reproduction, Ludwig Maximillian Universität, Munich, Germany, 2014.
Reproduced with permission from Ludwig Maximillian Universität.
516