Page 118 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 118
108 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
Metastatic deposits tend to lodge in the lymphatic always be detected on CT and MR images, and fine‐
sinuses of affected nodes, and when macrometastases needle aspiration cytology is necessary for diagnosis.
are present, filling defects can be identified on contrast‐ Lymphoma may also affect the lymph nodes of the
enhanced images. On CT images, these need to be dis- head and neck. Diffuse large‐cell B‐cell lymphoma
tinguished from fat within the lymph node hilus, which results in marked enlargement of the retropharyngeal
can mimic a parenchymal filling defect. On MR images and/or mandibular lymph node groups. The contrast
of dogs with mast cell tumors, affected lymph nodes enhancement in these lymph nodes is uniform with a
were larger and more heterogeneous on T2 and contrast‐ slightly foamy appearance. Small lymph nodes that are
enhanced images than normal lymph nodes. Lymph not normally identified, such as the parotid lymph node,
10
nodes in cats with metastatic disease from squamous cell may become visible with increased size (Figure 1.8.10).
carcinoma were not significantly larger than normal T‐cell lymphoma may affect a single lymph node in the
11
lymph nodes. Therefore, affected lymph nodes cannot head with similar imaging characteristics.
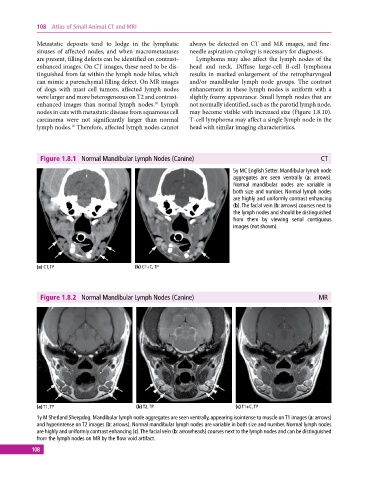
Figure 1.8.1 Normal Mandibular Lymph Nodes (Canine) CT
5y MC English Setter. Mandibular lymph node
aggregates are seen ventrally (a: arrows).
Normal mandibular nodes are variable in
both size and number. Normal lymph nodes
are highly and uniformly contrast enhancing
(b). The facial vein (b: arrows) courses next to
the lymph nodes and should be distinguished
from them by viewing serial contiguous
images (not shown).
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP
Figure 1.8.2 Normal Mandibular Lymph Nodes (Canine) MR
(a) T1, TP (b) T2, TP (c) T1+C, TP
1y M Shetland Sheepdog. Mandibular lymph node aggregates are seen ventrally, appearing isointense to muscle on T1 images (a: arrows)
and hyperintense on T2 images (b: arrows). Normal mandibular lymph nodes are variable in both size and number. Normal lymph nodes
are highly and uniformly contrast enhancing (c). The facial vein (b: arrowheads) courses next to the lymph nodes and can be distinguished
from the lymph nodes on MR by the flow void artifact.
108