Page 49 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 49
Ear 39
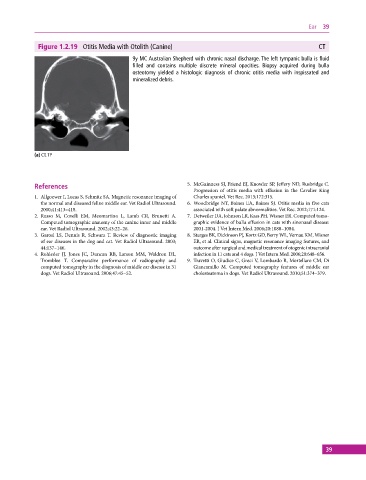
Figure 1.2.19 Otitis Media with Otolith (Canine) CT
9y MC Australian Shepherd with chronic nasal discharge. The left tympanic bulla is fluid
filled and contains multiple discrete mineral opacities. Biopsy acquired during bulla
osteotomy yielded a histologic diagnosis of chronic otitis media with inspissated and
mineralized debris.
(a) CT, TP
References 5. McGuinness SJ, Friend EJ, Knowler SP, Jeffery ND, Rusbridge C.
Progression of otitis media with effusion in the Cavalier King
1. Allgoewer I, Lucas S, Schmitz SA. Magnetic resonance imaging of Charles spaniel. Vet Rec. 2013;172:315.
the normal and diseased feline middle ear. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 6. Woodbridge NT, Baines EA, Baines SJ. Otitis media in five cats
2000;41:413–418. associated with soft palate abnormalities. Vet Rec. 2012;171:124.
2. Russo M, Covelli EM, Meomartino L, Lamb CR, Brunetti A. 7. Detweiler DA, Johnson LR, Kass PH, Wisner ER. Computed tomo
Computed tomographic anatomy of the canine inner and middle graphic evidence of bulla effusion in cats with sinonasal disease:
ear. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2002;43:22–26. 2001‐2004. J Vet Intern Med. 2006;20:1080–1084.
3. Garosi LS, Dennis R, Schwarz T. Review of diagnostic imaging 8. Sturges BK, Dickinson PJ, Kortz GD, Berry WL, Vernau KM, Wisner
of ear diseases in the dog and cat. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2003; ER, et al. Clinical signs, magnetic resonance imaging features, and
44:137–146. outcome after surgical and medical treatment of otogenic intracranial
4. Rohleder JJ, Jones JC, Duncan RB, Larson MM, Waldron DL, infection in 11 cats and 4 dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2006;20:648–656.
Tromblee T. Comparative performance of radiography and 9. Travetti O, Giudice C, Greci V, Lombardo R, Mortellaro CM, Di
computed tomography in the diagnosis of middle ear disease in 31 Giancamillo M. Computed tomography features of middle ear
dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2006;47:45–52. cholesteatoma in dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2010;51:374–379.
39