Page 205 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 205
208 13 Acquired Heart Disease
one peak due to an elevated heart rate found in cats.
Regurgitant flow at the mitral and tricuspid valves occurs
after valve closure and before the valves open again and
will be represented below the baseline on pulsed‐wave or
continuous‐wave Doppler (Figure 13.6). On color Doppler,
when the mitral and tricuspid valves are closed, abnormal
flow will be blue or a mosaic of colors, depending on the
velocity of the regurgitant flow (Figure 13.7). Normal lami
nar flow at the aortic valve will be below the baseline and
should not be greater than 1.2 m/s. Regurgitant blood flow
at the aortic valve will be above the baseline when the aor
tic valves are closed (Figure 13.8a). In order to document
left ventricular outflow obstruction, pulsed‐wave or con
tinuous‐wave Doppler is recorded and compared to the
Figure 13.4 Right parasternal longitudinal axis view depicting velocity at the level of the aortic valve.
the relationship of the left atrium (LA) to the left ventricle (LV). Color Doppler of regurgitant flow at the aortic valve
The size of the left atrium should be measured when the mitral
valves are closed. shows as a red jet traveling from the valve into the left
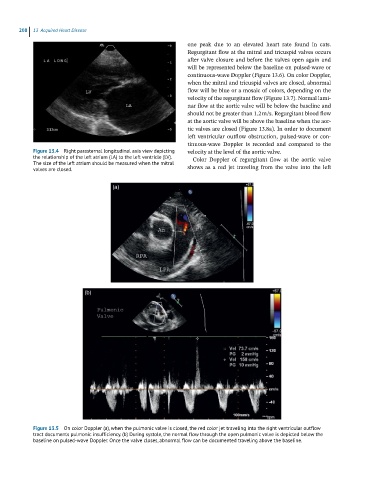
(a)
(b)
Figure 13.5 On color Doppler (a), when the pulmonic valve is closed, the red color jet traveling into the right ventricular outflow
tract documents pulmonic insufficiency. (b) During systole, the normal flow through the open pulmonic valve is depicted below the
baseline on pulsed-wave Doppler. Once the valve closes, abnormal flow can be documented traveling above the baseline.