Page 214 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 214
13.8 Hypertropcic bstructiOe Cardiomyopatcy, Asymmetric Hypertropcic Cardiomyopatcy 217
(b)
(a)
(c) (d)
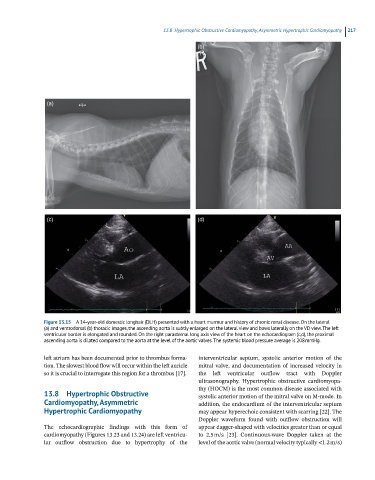
Figure 13.15 A 14-year-old domestic longhair (DLH) presented with a heart murmur and history of chronic renal disease. On the lateral
(a) and ventrodorsal (b) thoracic images, the ascending aorta is subtly enlarged on the lateral view and bows laterally on the VD view. The left
ventricular border is elongated and rounded. On the right parasternal long axis view of the heart on the echocardiogram (c,d), the proximal
ascending aorta is dilated compared to the aorta at the level of the aortic valves. The systemic blood pressure average is 208 mmHg.
left atrium has been documented prior to thrombus forma interventricular septum, systolic anterior motion of the
tion. The slowest blood flow will occur within the left auricle mitral valve, and documentation of increased velocity in
so it is crucial to interrogate this region for a thrombus [17]. the left ventricular outflow tract with Doppler
ultrasonography. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopa
thy (HOCM) is the most common disease associated with
13.8 Hypertrophic Obstructive systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve on M‐mode. In
Cardiomyopathy, Asymmetric addition, the endocardium of the interventricular septum
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy may appear hyperechoic consistent with scarring [22]. The
Doppler waveform found with outflow obstruction will
The echocardiographic findings with this form of appear dagger‐shaped with velocities greater than or equal
cardiomyopathy (Figures 13.23 and 13.24) are left ventricu to 2.5 m/s [23]. Continuous‐wave Doppler taken at the
lar outflow obstruction due to hypertrophy of the level of the aortic valve (normal velocity typically <1.2 m/s)