Page 269 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 269
14.6 Pneumonia 273
A cranioventral distribution is common, likely due to 14.6.2 Fungal Pneumonia
decreased local defense mechanisms (effect of gravity on 14.6.2.1 Histoplasmosis
normal clearance mechanisms) in the cranioventral lobes
[57]. The dependent portions of the right middle and left Histoplasmosis is a systemic fungal infection caused by
Histoplasma capsulatum, with infection primarily in
and right cranial lung lobes are most commonly affected
with aspiration pneumonia. An alveolar pattern is com- endemic areas (Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi river val-
leys). The route of entry is usually respiratory (inhalation
mon, but a mixed interstitial/bronchial pattern, with or
without an alveolar component and/or lobar consolida- of spores), in some cases resulting in pulmonary granu-
lomatous disease. Dissemination to lymph nodes, liver,
tion, can also be present [12,50,52,57]. It can be difficult to
differentiate infectious pneumonia from diffuse or focal spleen, bone marrow, eyes, skin, and bone is possible [58].
Radiographic changes are variable, but a diffuse miliary
neoplasia on the basis of radiographs alone [12].
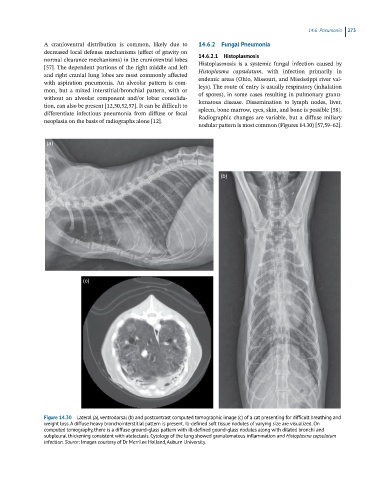
nodular pattern is most common (Figures 14.30) [57,59–62].
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 14.30 Lateral (a), ventrodorsal (b) and postcontrast computed tomographic image (c) of a cat presenting for difficult breathing and
weight loss. A diffuse heavy bronchointerstitial pattern is present. Ill-defined soft tissue nodules of varying size are visualized. On
computed tomography, there is a diffuse ground-glass pattern with ill-defined gound-glass nodules along with dilated bronchi and
subpleural thickening consistent with atelectasis. Cytology of the lung showed granulomatous inflammation and Histoplasma capsulatum
infection. Source: Images courtesy of Dr Merrilee Holland, Auburn University.