Page 380 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 380
23.5 epatic Ultrasound 389
hepatis and branches (Figure 23.14). The bile duct, a small parenchyma. Hepatic vein borders are not echogenic, with
anechoic tubular structure surrounded by hyperechoic the exception of the veins near their confluence with the
fat, can be imaged immediately ventral to the portal vein caudal vena cava, immediately adjacent to the diaphragm
in this window, and followed to the duodenal papilla. [44]. Normal hepatic arteries are not typically visualized
Peripheral portal veins are smoothly tapering vessels char- without color Doppler examination.
acterized by bright, echogenic borders [44]. The larger left The gallbladder is well visualized as an oval to pear‐
and smaller right branch originate from the main portal shaped, anechoic structure in the right cranioventral por-
vein near the porta hepatis, although they branch in dif- tion of the liver (Figure 23.16). Gallbladder size can vary
ferent imaging planes (Figure 23.15). Hepatic veins appear significantly. Intraluminal contents are typically ane-
as anechoic linear structures extending through the choic, although occasionally gallbladder sludge (dependent
(a) (b)
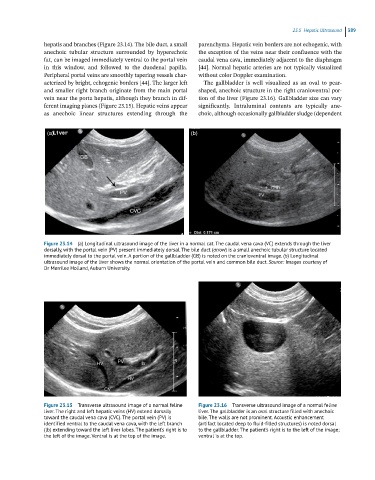
Figure 23.14 (a) Longitudinal ultrasound image of the liver in a normal cat. The caudal vena cava (VC) extends through the liver
dorsally, with the portal vein (PV) present immediately dorsal. The bile duct (arrow) is a small anechoic tubular structure located
immediately dorsal to the portal vein. A portion of the gallbladder (GB) is noted on the cranioventral image. (b) Longitudinal
ultrasound image of the liver shows the normal orientation of the portal vein and common bile duct. Source: Images courtesy of
Dr Merrilee Holland, Auburn University.
Figure 23.15 Transverse ultrasound image of a normal feline Figure 23.16 Transverse ultrasound image of a normal feline
liver. The right and left hepatic veins (HV) extend dorsally liver. The gallbladder is an oval structure filled with anechoic
toward the caudal vena cava (CVC). The portal vein (PV) is bile. The walls are not prominent. Acoustic enhancement
identified ventral to the caudal vena cava, with the left branch (artifact located deep to fluid-filled structures) is noted dorsal
(lb) extending toward the left liver lobes. The patient’s right is to to the gallbladder. The patient’s right is to the left of the image;
the left of the image. Ventral is at the top of the image. ventral is at the top.