Page 104 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 104
88 Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant
returning to normal when operations of the body are facilitate the flight or fight response. The pancreas is
switched back to the parasympathetic nervous system. a gland that produces insulin to maintain blood sugar
How does all these things happen? How do muscle levels. Not enough insulin leads to diabetes mellitus.
move? What prompts a swallow? The CNS is made up of The gonads are sex glands that produce the hormones
millions of neurons (Figure 5.23). The neurons of the a male and female need to be able to reproduce.
spinal cord branch off through the body and this is Diseases of the glands cause hypothyroidism or hyper-
referred to as the peripheral nervous system. The pro- thyroidism, too little or too much thyroid hormone. Too
cess of nerves bringing or sending signals to and from an much adrenal hormone or hyperadrenocorticism leads
area of the body is called enervation. Enervation can to Cushing’s disease. Too little adrenal hormone or
come from the CNS or it can come from the peripheral hypoadrenocorticism leads to Addison’s disease.
nerves back to the CNS. Impulses sent along the neurons Blood tests can determine which hormone is missing,
are carried by chemical messengers called neurotrans- low, or elevated and the veterinarian is usually able to
mitters. Neurotransmitters are serotonin, dopamine, treat the animal with medication to control the disease
acetylcholine, norepinephrine, gamma‐aminobutyric process. However, that animal may be on a medication
acid, and glutamate. Each has a different job; for for life.
example, serotonin is responsible for sleep, mood, appe-
tite, temperature regulation, sensory perception, and Integumentary System
pain suppression. The neurotransmitter travels along
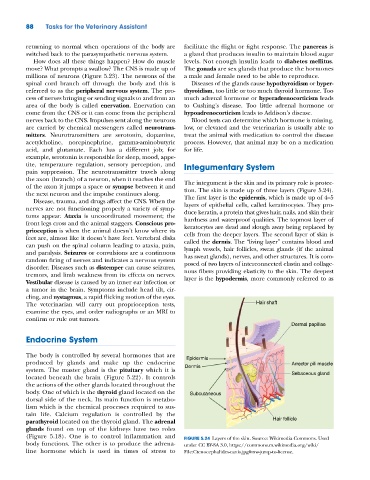
the axon (branch) of a neuron, when it reaches the end The integument is the skin and its primary role is protec-
of the axon it jumps a space or synapse between it and tion. The skin is made up of three layers (Figure 5.24).
the next neuron and the impulse continues along. The first layer is the epidermis, which is made up of 4–5
Disease, trauma, and drugs affect the CNS. When the
nerves are not functioning properly a variety of symp- layers of epithelial cells, called keratinocytes. They pro-
duce keratin, a protein that gives hair, nails, and skin their
toms appear. Ataxia is uncoordinated movement; the hardness and waterproof qualities. The topmost layer of
front legs cross and the animal staggers. Conscious pro- keratocytes are dead and slough away being replaced by
prioception is when the animal doesn’t know where its cells from the deeper layers. The second layer of skin is
feet are, almost like it doesn’t have feet. Vertebral disks called the dermis. The “living layer” contains blood and
can push on the spinal column leading to ataxia, pain, lymph vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands (if the animal
and paralysis. Seizures or convulsions are a continuous has sweat glands), nerves, and other structures. It is com-
random firing of nerves and indicates a nervous system posed of two layers of interconnected elastin and collage-
disorder. Diseases such as distemper can cause seizures, nous fibers providing elasticity to the skin. The deepest
tremors, and limb weakness from its effects on nerves. layer is the hypodermis, more commonly referred to as
Vestibular disease is caused by an inner ear infection or
a tumor in the brain. Symptoms include head tilt, cir-
cling, and nystagmus, a rapid flicking motion of the eyes.
The veterinarian will carry out proprioception tests, Hair shaft
examine the eyes, and order radiographs or an MRI to
confirm or rule out tumors.
Dermal papillae
Endocrine System
The body is controlled by several hormones that are Epidermis
produced by glands and make up the endocrine Arrector pili muscle
system. The master gland is the pituitary which it is Dermis
located beneath the brain (Figure 5.22). It controls Sebaceous gland
the actions of the other glands located throughout the
body. One of which is the thyroid gland located on the Subcutaneous
dorsal side of the neck. Its main function is metabo-
lism which is the chemical processes required to sus-
tain life. Calcium regulation is controlled by the
parathyroid located on the thyroid gland. The adrenal Hair follicle
glands found on top of the kidneys have two roles
(Figure 5.18). One is to control inflammation and FIGURE 5.24 Layers of the skin. Source: Wikimedia Commons. Used
body functions. The other is to produce the adrena- under CC BY‐SA 3.0, https://commons.m.wikimedia.org/wiki/
line hormone which is used in times of stress to File:Ctenocephalides‐canis.jpg#mw‐jump‐to‐license.