Page 101 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 101
Chapter 5 Anatomy and Physiology 85
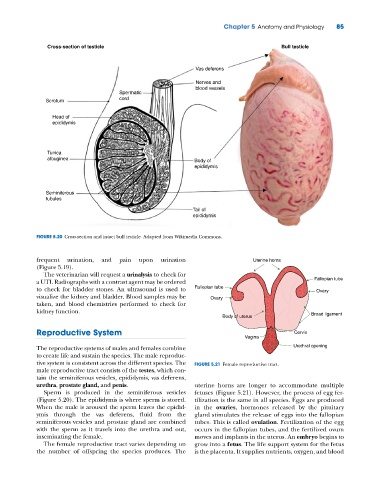
Cross-section of testicle Bull testicle
Vas deferens
Nerves and
blood vessels
Spermatic
Scrotum cord
Head of
epididymis
Tunica
albuginea Body of
epididymis
Seminiferous
tubules
Tail of
epididymis
FIGURE 5.20 Cross‐section and intact bull testicle. Adapted from Wikimedia Commons.
frequent urination, and pain upon urination Uterine horns
(Figure 5.19).
The veterinarian will request a urinalysis to check for
a UTI. Radiographs with a contrast agent may be ordered Fallopian tube
to check for bladder stones. An ultrasound is used to Fallopian tube Ovary
visualize the kidney and bladder. Blood samples may be Ovary
taken, and blood chemistries performed to check for
kidney function.
Body of uterus Broad ligament
Reproductive System Cervix
Vagina
The reproductive systems of males and females combine Urethral opening
to create life and sustain the species. The male reproduc-
tive system is consistent across the different species. The FIGURE 5.21 Female reproductive tract.
male reproductive tract consists of the testes, which con-
tain the seminiferous vesicles, epididymis, vas deferens,
urethra, prostate gland, and penis. uterine horns are longer to accommodate multiple
Sperm is produced in the seminiferous vesicles fetuses (Figure 5.21). However, the process of egg fer-
(Figure 5.20). The epididymis is where sperm is stored. tilization is the same in all species. Eggs are produced
When the male is aroused the sperm leaves the epidid- in the ovaries, hormones released by the pituitary
ymis through the vas deferens, fluid from the gland stimulates the release of eggs into the fallopian
seminiferous vesicles and prostate gland are combined tubes. This is called ovulation. Fertilization of the egg
with the sperm as it travels into the urethra and out, occurs in the fallopian tubes, and the fertilized ovum
inseminating the female. moves and implants in the uterus. An embryo begins to
The female reproductive tract varies depending on grow into a fetus. The life support system for the fetus
the number of offspring the species produces. The is the placenta. It supplies nutrients, oxygen, and blood