Page 97 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 97
Chapter 5 Anatomy and Physiology 81
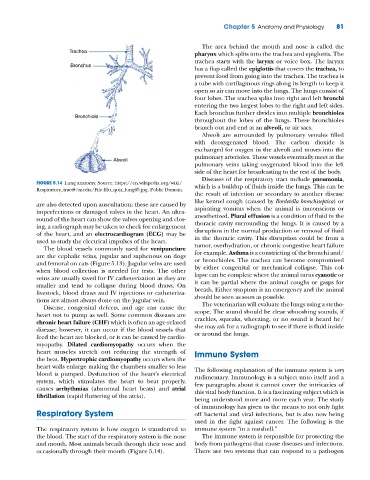
The area behind the mouth and nose is called the
Trachea
pharynx which splits into the trachea and epiglottis. The
trachea starts with the larynx or voice box. The larynx
Bronchus
has a flap called the epiglottis that covers the trachea, to
prevent food from going into the trachea. The trachea is
a tube with cartilaginous rings along its length to keep it
open so air can move into the lungs. The lungs consist of
four lobes. The trachea splits into right and left bronchi
entering the two largest lobes to the right and left sides.
Each bronchus further divides into multiple bronchioles
Bronchiole
throughout the lobes of the lungs. These bronchioles
branch out and end at an alveoli, or air sacs.
Alveoli are surrounded by pulmonary venules filled
with deoxygenated blood. The carbon dioxide is
exchanged for oxygen in the alveoli and moves into the
pulmonary arterioles. These vessels eventually meet at the
Alveoli
pulmonary veins taking oxygenated blood into the left
side of the heart for broadcasting to the rest of the body.
Diseases of the respiratory tract include pneumonia,
FIGURE 5.14 Lung anatomy. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ which is a buildup of fluids inside the lungs. This can be
Respiratory_tract#/media/File:Illu_quiz_lung05.jpg. Public Domain.
the result of infection or secondary to another disease
like kennel cough (caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica) or
are also detected upon auscultation; these are caused by
imperfections or damaged valves in the heart. An ultra- aspirating vomitus when the animal is unconscious or
sound of the heart can show the valves opening and clos- anesthetized. Plural effusion is a condition of fluid in the
ing, a radiograph may be taken to check for enlargement thoracic cavity surrounding the lungs. It is caused by a
of the heart, and an electrocardiogram (ECG) may be disruption in the normal production or removal of fluid
used to study the electrical impulses of the heart. in the thoracic cavity. This disruption could be from a
The blood vessels commonly used for venipuncture tumor, overhydration, or chronic congestive heart failure
are the cephalic veins, jugular and saphenous on dogs for example. Asthma is a constricting of the bronchi and/
and femoral on cats (Figure 5.13). Jugular veins are used or bronchioles. The trachea can become compromised
when blood collection is needed for tests. The other by either congenital or mechanical collapse. This col-
veins are usually saved for IV catheterization as they are lapse can be complete where the animal turns cyanotic or
smaller and tend to collapse during blood draws. On it can be partial where the animal coughs or gasps for
livestock, blood draws and IV injections or catheteriza- breath. Either symptom is an emergency and the animal
tions are almost always done on the jugular vein. should be seen as soon as possible.
Disease, congenital defects, and age can cause the The veterinarian will evaluate the lungs using a stetho-
heart not to pump as well. Some common diseases are scope. The sound should be clear whooshing sounds, if
chronic heart failure (CHF) which is often an age‐related crackles, squeaks, wheezing, or no sound is heard he/
disease; however, it can occur if the blood vessels that she may ask for a radiograph to see if there is fluid inside
feed the heart are blocked, or it can be caused by cardio- or around the lungs.
myopathy. Dilated cardiomyopathy occurs when the
heart muscles stretch out reducing the strength of Immune System
the beat. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy occurs when the
heart walls enlarge making the chambers smaller so less The following explanation of the immune system is very
blood is pumped. Dysfunction of the heart’s electrical rudimentary. Immunology is a subject unto itself and a
system, which stimulates the heart to beat properly, few paragraphs about it cannot cover the intricacies of
causes arrhythmias (abnormal heart beats) and atrial this vital body function. It is a fascinating subject which is
fibrillation (rapid fluttering of the atria).
being understood more and more each year. The study
of immunology has given us the means to not only fight
Respiratory System off bacterial and viral infections, but is also now being
used in the fight against cancer. The following is the
The respiratory system is how oxygen is transferred to immune system “in a nutshell.”
the blood. The start of the respiratory system is the nose The immune system is responsible for protecting the
and mouth. Most animals breath through their nose and body from pathogens that cause diseases and infections.
occasionally through their mouth (Figure 5.14). There are two systems that can respond to a pathogen