Page 694 - Microeconomics, Fourth Edition
P. 694
c16GeneralEquilibriumTheory.qxd 8/16/10 9:13 PM Page 668
668 CHAPTER 16 GENERAL EQUILIBRIUM THEORY
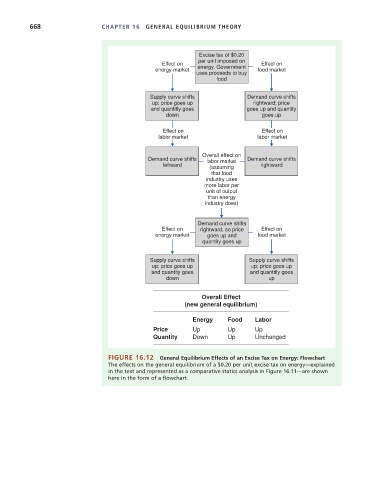
Excise tax of $0.20
per unit imposed on
Ef fect on Ef fect on
energy market energy . Government food market
uses proceeds to buy
food
Supply curve shifts Demand curve shifts
up; price goes up rightward; price
and quantitly goes goes up and quantity
dow n goes up
Ef fect on Ef fect on
labor market labor market
Overall ef fect on
Demand curve shifts labor market Demand curve shifts
leftward (assumin g rightward
that food
industry uses
more labor per
unit of output
than energy
industry does)
Demand curve shifts
Ef fect on rightward, so price Ef fect on
energy market goes up and food market
quantity goes up
Supply curve shifts Supply curve shifts
up; price goes up up; price goes up
and quantity goes and quantitly goes
dow n up
Overall Effect
(new general equilibrium)
Energy Food Labor
Price Up Up Up
Quantity Down Up Unchanged
FIGURE 16.12 General Equilibrium Effects of an Excise Tax on Energy: Flowchart
The effects on the general equilibrium of a $0.20 per unit excise tax on energy—explained
in the text and represented as a comparative statics analysis in Figure 16.11—are shown
here in the form of a flowchart.