Page 17 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 10
P. 17
LOS 38.a: Describe credit default swaps READING 38: CREDIT DEFAULT SWAPS
(CDS), single-name and index CDS, and the
parameters that define a given CDS product. MODULE 38.1: CDS FEATURES AND
TERMS
A credit protection seller receives a premium (CDS spread) and insures a credit protection buyer against credit risk/default that may
arise from a reference entity that issued/sold a fixed income security or bond (to such credit protection buyer). The contract is written
on the face value of the protection (notional principal). Doesn’t cover market-wide interest rate risk! The protection seller is long
credit risk, while the buyer is short credit risk. Why Swaps?
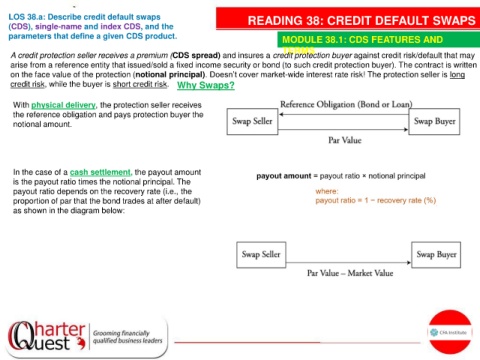
With physical delivery, the protection seller receives
the reference obligation and pays protection buyer the
notional amount.
In the case of a cash settlement, the payout amount
is the payout ratio times the notional principal. The
payout ratio depends on the recovery rate (i.e., the
proportion of par that the bond trades at after default)
as shown in the diagram below: