Page 12 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 10
P. 12
LOS 37.e: Calculate the value of a bond READING 37: CREDIT ANALYSIS MODELS
and its credit spread, given assumptions
about the credit risk parameters.
MODULE 37.5: CREDIT SPREAD ANALYSIS
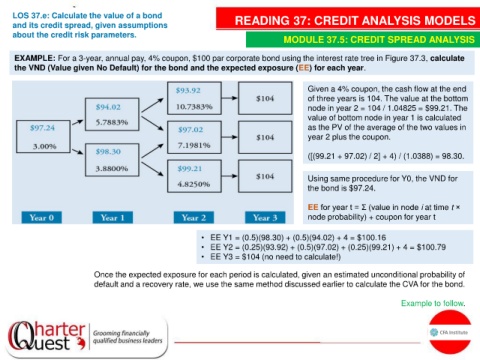
EXAMPLE: For a 3-year, annual pay, 4% coupon, $100 par corporate bond using the interest rate tree in Figure 37.3, calculate
the VND (Value given No Default) for the bond and the expected exposure (EE) for each year.
Given a 4% coupon, the cash flow at the end
of three years is 104. The value at the bottom
node in year 2 = 104 / 1.04825 = $99.21. The
value of bottom node in year 1 is calculated
as the PV of the average of the two values in
year 2 plus the coupon.
([(99.21 + 97.02) / 2] + 4) / (1.0388) = 98.30.
Using same procedure for Y0, the VND for
the bond is $97.24.
EE for year t = Σ (value in node i at time t ×
node probability) + coupon for year t
• EE Y1 = (0.5)(98.30) + (0.5)(94.02) + 4 = $100.16
• EE Y2 = (0.25)(93.92) + (0.5)(97.02) + (0.25)(99.21) + 4 = $100.79
• EE Y3 = $104 (no need to calculate!)
Once the expected exposure for each period is calculated, given an estimated unconditional probability of
default and a recovery rate, we use the same method discussed earlier to calculate the CVA for the bond.
Example to follow.