Page 9 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 10
P. 9
LOS 37.d: Explain structural and reduced-form READING 37: CREDIT ANALYSIS MODELS
models of corporate credit risk, including
assumptions, strengths, and weaknesses. MODULE 37.4: STRUCTURAL AND REDUCED FORM MODELS
Alternatively, equity investors are long the net assets of the company (with a time T value of A – D) and long a put option,
T
allowing them to sell the assets at an exercise price of D.
Under this analogy, the investors in risky debt can be construed
Default is then synonymous to exercising the put option: to have a long position in risk-free debt and a short position in
that put option.
value of the put option = max (0, K – A )
T
value of risky debt = value of risk-free debt – value of put option
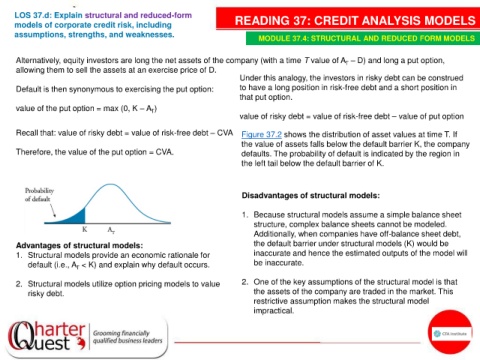
Recall that: value of risky debt = value of risk-free debt – CVA Figure 37.2 shows the distribution of asset values at time T. If
the value of assets falls below the default barrier K, the company
Therefore, the value of the put option = CVA. defaults. The probability of default is indicated by the region in
the left tail below the default barrier of K.
Disadvantages of structural models:
1. Because structural models assume a simple balance sheet
structure, complex balance sheets cannot be modeled.
Additionally, when companies have off-balance sheet debt,
Advantages of structural models: the default barrier under structural models (K) would be
1. Structural models provide an economic rationale for inaccurate and hence the estimated outputs of the model will
default (i.e., A < K) and explain why default occurs. be inaccurate.
T
2. Structural models utilize option pricing models to value 2. One of the key assumptions of the structural model is that
risky debt. the assets of the company are traded in the market. This
restrictive assumption makes the structural model
impractical.