Page 11 - FINAL CFA II SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 10
P. 11
LOS 37.e: Calculate the value of a bond READING 37: CREDIT ANALYSIS MODELS
and its credit spread, given assumptions
about the credit risk parameters.
MODULE 37.5: CREDIT SPREAD ANALYSIS
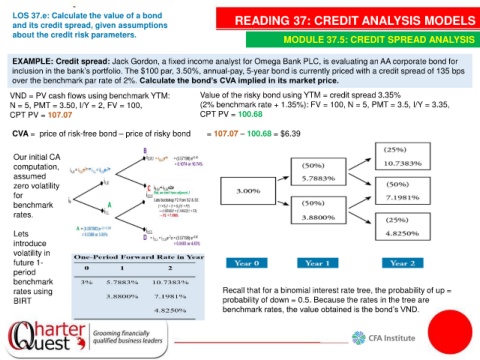
EXAMPLE: Credit spread: Jack Gordon, a fixed income analyst for Omega Bank PLC, is evaluating an AA corporate bond for
inclusion in the bank’s portfolio. The $100 par, 3.50%, annual-pay, 5-year bond is currently priced with a credit spread of 135 bps
over the benchmark par rate of 2%. Calculate the bond’s CVA implied in its market price.
VND = PV cash flows using benchmark YTM: Value of the risky bond using YTM = credit spread 3.35%
N = 5, PMT = 3.50, I/Y = 2, FV = 100, (2% benchmark rate + 1.35%): FV = 100, N = 5, PMT = 3.5, I/Y = 3.35,
CPT PV = 107.07 CPT PV = 100.68
CVA = price of risk-free bond – price of risky bond = 107.07 – 100.68 = $6.39
Our initial CA
computation,
assumed
zero volatility
for
benchmark
rates.
Lets
introduce
volatility in
future 1-
period
benchmark
rates using Recall that for a binomial interest rate tree, the probability of up =
BIRT probability of down = 0.5. Because the rates in the tree are
benchmark rates, the value obtained is the bond’s VND.