Page 28 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 28
LOS 34.l: Explain how a bond’s exposure to each of the READING 34: THE TERM STRUCTURE AND
factors driving the yield curve can be measured and how these INTEREST RATE DYNAMICS
exposures can be used to manage yield curve risks.
MODULE 34.6: INTEREST RATE MODELS
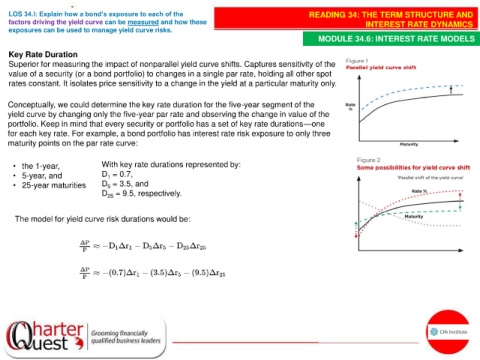
Key Rate Duration
Superior for measuring the impact of nonparallel yield curve shifts. Captures sensitivity of the
value of a security (or a bond portfolio) to changes in a single par rate, holding all other spot
rates constant. It isolates price sensitivity to a change in the yield at a particular maturity only.
Conceptually, we could determine the key rate duration for the five-year segment of the
yield curve by changing only the five-year par rate and observing the change in value of the
portfolio. Keep in mind that every security or portfolio has a set of key rate durations—one
for each key rate. For example, a bond portfolio has interest rate risk exposure to only three
maturity points on the par rate curve:
• the 1-year, With key rate durations represented by:
• 5-year, and D = 0.7,
1
• 25-year maturities D = 3.5, and
5
D 25 = 9.5, respectively.
The model for yield curve risk durations would be: