Page 22 - DIVA_1_2009
P. 22
Oil and gas production increasingly in the
hands of developing countries
Until the 1970s, a few major including the so-called
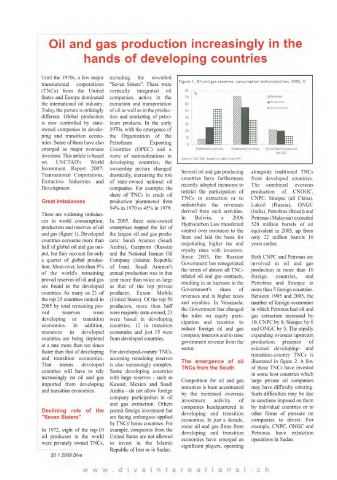
Figure 1. Oil and gas reserves, consumption and production, 2005, %
transnational corporations "Seven Sisters". These were
(TNCs) from the United vertically integrated oil 80
States and Europe dominated companies, active in the 70 2 Reser*s
the international oil industry. extraction and transportation 60 I Produ0000
le ConS ursp000
Today, the picture is strikingly of oil as well as in the produc- 50
different. Global production tion and marketing of petro- 40
is now controlled by state- leum products. In the early 30
owned companies in develo- 1970s, with the emergence of 20
ping and transition econo- the Organization of the 10
mies. Some of them have also Petroleum Exporting
0
emerged as major overseas Countries (OPEC) and a Developed Countries South-East Europe and
Developing c000tnes
the CIS
investors. This article is based wave of nationalizations in
Source UNCTAD, based on data from IHS.
on IJNCTAD's World developing countries, the
Investment Report 2007: ownership picture changed
Several oil and gas producing alongside traditional TNCs
Transnational Corporations, drastically, increasing the role
countries have furthermore from developed countries.
Extractive Industries and of state-owned national oil
recently adopted measures to The combined overseas
Development. companies. For example, the
restrict the participation of production of CNOOC,
share of TNCs in crude oil
TNCs in extraction or to CNPC, Sinopec (all China),
Great imbalances production plummeted from
redistribute the revenues Lukoil (Russia), ONGC
94% in 1970to45%in 1979.
There are widening imbalan- derived from such activities. (India), Petrobras (Brazil) and
In Bolivia, a 2006 Petronas (Malaysia) exceeded
ces in world consumption, In 2005, three state-owned
Hydrocarbon Law transferred 528 million barrels of oil
production and reserves of oil enterprises topped the list of
control over resources to the equivalent in 2005, up from
and gas (figure 1). Developed the largest oil and gas produ-
State and laid the basis for only 22 million barrels 10
countries consume more than cers: Saudi Aramco (Saudi
negotiating higher tax and years earlier.
half of global oil and gas out- Arabia), Gazprom (Russia)
royalty rates with investors.
put, but they account for only and the National Iranian Oil
Since 2003, the Russian Both CNPC and Petronas are
a quarter of global produc- Company (Islamic Republic Government has renegotiated involved in oil and gas
tion. More-over, less than 8% of Iran). Saudi Aramco's
the terms of almost all TNC- production in more than 10
of the world's remaining annual production was in that
related oil and gas contracts, foreign countries, and
proved reserves of oil and gas year more than twice as large
resulting in an increase in the Petrobras and Sinopec in
are found in the developed as that of the top private
Government's share of more than 5 foreign countries.
countries. As many as 21 of producer, Exxon Mobile
revenues and in higher taxes Between 1995 and 2005, the
the top 25 countries ranked in (United States). Of the top 50
and royalties. In Venezuela, number of foreign economies
2005 by total remaining pro- producers, more than half
the Government has changed in which Petronas had oil and
were were majority state-owned, 23
ved the rules on equity parti- gas extraction increased by
reserves
developing or transition were based in developing
cipation and taxation to 10, CNPC by 8, Sinopec by 6
economies. In addition, countries, 12 in transition
reduce foreign oil and gas and ONGC by 5. The rapidly
resources in developed economies and just 15 were
company interests and to raise expanding overseas upstream
countries are being depleted from developed countries.
government revenue from the production presence of
at a rate more than ten times
sector. selected developing- and
faster than that of developing For developed-country TNCs,
transition-country TNCs is
and transition economies. accessing remaining reserves
The emergence of oil illustrated in figure 2. A few
That means developed is also increasingly complex.
TNCs from the South of these TNCs have invested
countries will have to rely Some developing countries
in some host countries which
increasingly on oil and gas with large reserves - such as
Competition for oil and gas large private oil companies
imported from developing Kuwait, Mexico and Saudi
resources is been accentuated may have difficulty entering.
and transition economies. Arabia - do not allow foreign
by the increased overseas Such difficulties may be due
company participation in oil
investment activity of to sanctions imposed on them
and gas extraction. Others
companies headquartered in by individual countries or to
Declining role of the permit foreign investment but
developing and transition other forms of pressure on
"Seven Sisters" are facing embargoes applied
economies. In just a decade, companies to divest. For
by TNCs' home countries. For
some oil and gas firms from example, CNPC, ONGC and
In 1972, eight of the top-10 example, companies from the
developing and transition Petronas have extraction
oil producers in the world United States are not allowed
economies have emerged as operations in Sudan.
were privately owned TNCs, to invest in the Islamic
significant players, operating
Republic of Iran or in Sudan.
20 12009 Diva
vain t n a t i o n a I
c h