Page 155 - Basic Monitoring in Canine and Feline Emergency Patients
P. 155
3
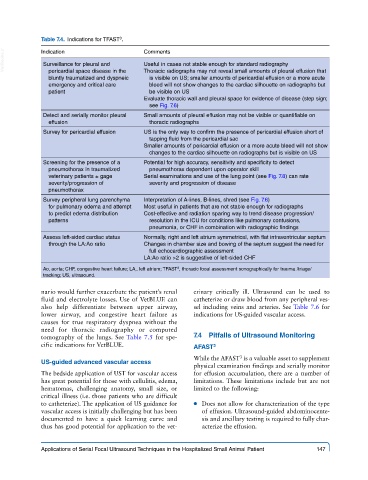
Table 7.4. Indications for TFAST .
VetBooks.ir Indication Comments
Useful in cases not stable enough for standard radiography
Surveillance for pleural and
pericardial space disease in the
is visible on US; smaller amounts of pericardial effusion or a more acute
bluntly traumatized and dyspneic Thoracic radiographs may not reveal small amounts of pleural effusion that
emergency and critical care bleed will not show changes to the cardiac silhouette on radiographs but
patient be visible on US
Evaluate thoracic wall and pleural space for evidence of disease (step sign;
see Fig. 7.6)
Detect and serially monitor pleural Small amounts of pleural effusion may not be visible or quantifiable on
effusion thoracic radiographs
Survey for pericardial effusion US is the only way to confirm the presence of pericardial effusion short of
tapping fluid from the pericardial sac
Smaller amounts of pericardial effusion or a more acute bleed will not show
changes to the cardiac silhouette on radiographs but is visible on US
Screening for the presence of a Potential for high accuracy, sensitivity and specificity to detect
pneumothorax in traumatized pneumothorax dependent upon operator skill
veterinary patients ± gage Serial examinations and use of the lung point (see Fig. 7.8) can rate
severity/progression of severity and progression of disease
pneumothorax
Survey peripheral lung parenchyma Interpretation of A-lines, B-lines, shred (see Fig. 7.6)
for pulmonary edema and attempt Most useful in patients that are not stable enough for radiographs
to predict edema distribution Cost-effective and radiation sparing way to trend disease progression/
patterns resolution in the ICU for conditions like pulmonary contusions,
pneumonia, or CHF in combination with radiographic findings
Assess left-sided cardiac status Normally, right and left atrium symmetrical, with flat intraventricular septum
through the LA:Ao ratio Changes in chamber size and bowing of the septum suggest the need for
full echocardiographic assessment
LA:Ao ratio >2 is suggestive of left-sided CHF
3
Ao, aorta; CHF, congestive heart failure; LA,. left atrium; TFAST , thoracic focal assessment sonographically for trauma /triage/
tracking; US, ultrasound.
nario would further exacerbate the patient’s renal erinary critically ill. Ultrasound can be used to
fluid and electrolyte losses. Use of VetBLUE can catheterize or draw blood from any peripheral ves-
also help differentiate between upper airway, sel including veins and arteries. See Table 7.6 for
lower airway, and congestive heart failure as indications for US-guided vascular access.
causes for true respiratory dyspnea without the
need for thoracic radiography or computed
tomography of the lungs. See Table 7.5 for spe- 7.4 Pitfalls of Ultrasound Monitoring
cific indications for VetBLUE. AFAST 3
While the AFAST is a valuable asset to supplement
3
US-guided advanced vascular access
physical examination findings and serially monitor
The bedside application of UST for vascular access for effusion accumulation, there are a number of
has great potential for those with cellulitis, edema, limitations. These limitations include but are not
hematomas, challenging anatomy, small size, or limited to the following:
critical illness (i.e. those patients who are difficult
to catheterize). The application of US guidance for ● ● Does not allow for characterization of the type
vascular access is initially challenging but has been of effusion. Ultrasound-guided abdominocente-
documented to have a quick learning curve and sis and ancillary testing is required to fully char-
thus has good potential for application to the vet- acterize the effusion.
Applications of Serial Focal Ultrasound Techniques in the Hospitalized Small Animal Patient 147