Page 582 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 582
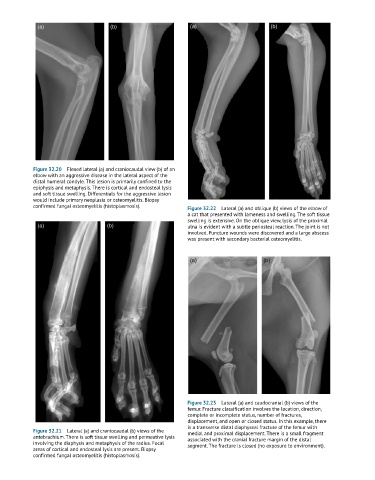
Figure 32.20 Flexed lateral (a) and craniocaudal view (b) of an
elbow with an aggressive disease in the lateral aspect of the
distal humeral condyle. This lesion is primarily confined to the
epiphysis and metaphysis. There is cortical and endosteal lysis
and soft tissue swelling. Differentials for the aggressive lesion
would include primary neoplasia or osteomyelitis. Biopsy
confirmed fungal osteomyelitis (histoplasmosis). Figure 32.22 Lateral (a) and oblique (b) views of the elbow of
a cat that presented with lameness and swelling. The soft tissue
swelling is extensive. On the oblique view, lysis of the proximal
ulna is evident with a subtle periosteal reaction. The joint is not
involved. Puncture wounds were discovered and a large abscess
was present with secondary bacterial osteomyelitis.
Figure 32.23 Lateral (a) and caudocranial (b) views of the
femur. Fracture classification involves the location, direction,
complete or incomplete status, number of fractures,
displacement, and open or closed status. In this example, there
is a transverse distal diaphyseal fracture of the femur with
Figure 32.21 Lateral (a) and craniocaudal (b) views of the medial and proximal displacement. There is a small fragment
antebrachium. There is soft tissue swelling and permeative lysis associated with the cranial fracture margin of the distal
involving the diaphysis and metaphysis of the radius. Focal segment. The fracture is closed (no exposure to environment).
areas of cortical and endosteal lysis are present. Biopsy
confirmed fungal osteomyelitis (histoplasmosis).