Page 178 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 178
146 Section 3 Cardiovascular Disease
When the PW Doppler mode is used, the velocity spec- lesion severity (Figure 16.26c). Pulmonic stenosis is
VetBooks.ir trum is broadened, as the flow is turbulent (instead of considered as severe when the pressure gradient across
the stenotic orifice exceeds 80–100 mmHg. Color flow
laminar). Measurement of peak velocity using the CW
Doppler mode and subsequent calculation of the maxi-
tolic pulmonary flow map, and is therefore useful to
mum systolic pressure gradient across the stenotic Doppler mode shows narrowing of the color‐coded sys-
lesion provides an accurate and noninvasive estimate of accurately localize the stenotic lesion (Figure 16.26b).
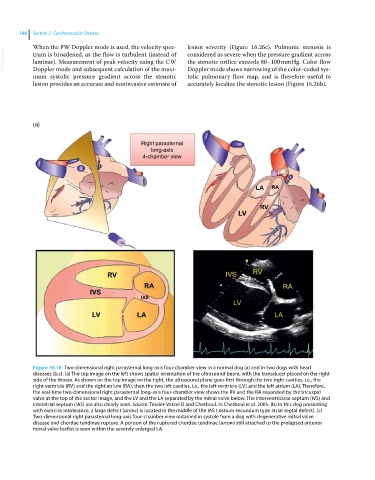
(a)
Right parasternal
long-axis
4-chamber view
Figure 16.16 Two‐dimensional right parasternal long‐axis four‐chamber view in a normal dog (a) and in two dogs with heart
diseases (b,c). (a) The top image on the left shows spatial orientation of the ultrasound beam, with the transducer placed on the right
side of the thorax. As shown on the top image on the right, the ultrasound plane goes first through the two right cavities, i.e., the
right ventricle (RV) and the right atrium (RA), then the two left cavities, i.e., the left ventricle (LV) and the left atrium (LA). Therefore,
the real‐time two‐dimensional right parasternal long‐axis four‐chamber view shows the RV and the RA separated by the tricuspid
valve at the top of the sector image, and the LV and the LA separated by the mitral valve below. The interventricular septum (IVS) and
interatrial septum (IAS) are also clearly seen. Source: Tessier-Vetzel D and Chetboul. In Chetboul et al. 2005. (b) In this dog presenting
with exercise intolerance, a large defect (arrow) is located in the middle of the IAS ( ostium secundum type atrial septal defect). (c)
Two‐dimensional right parasternal long‐axis four‐chamber view obtained in systole from a dog with degenerative mitral valve
disease and chordae tendinae rupture. A portion of the ruptured chordae tendinae (arrow) still attached to the prolapsed anterior
mitral valve leaflet is seen within the severely enlarged LA.