Page 299 - Essential Haematology
P. 299
Chapter 21 Multiple myeloma and related disorders / 285
with myeloma or Waldenstr ö m ’ s macroglobulinae-
mia or in patients with chronic myeloid or acute
leukaemias associated with very high white cell
counts.
The clinical features of the hyperviscosity
syndrome include visual disturbances, lethargy,
confusion, muscle weakness, nervous system symp-
toms and signs, and congestive heart failure. Th e
retina may show a variety of changes: engorged
veins, haemorrhages, exudates and a blurred disc
(Fig. 21.13 ).
Emergency treatment varies with the cause:
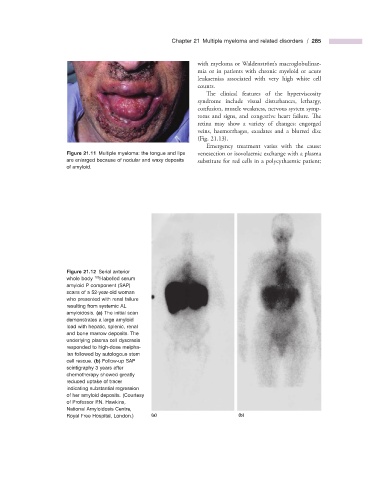
Figure 21.11 Multiple myeloma: the tongue and lips venesection or isovolaemic exchange with a plasma
are enlarged because of nodular and waxy deposits substitute for red cells in a polycythaemic patient;
of amyloid.
Figure 21.12 Serial anterior
123
whole body I - labelled serum
amyloid P component (SAP)
scans of a 52 - year - old woman
who presented with renal failure
resulting from systemic AL
amyloidosis. (a) The initial scan
demonstrates a large amyloid
load with hepatic, splenic, renal
and bone marrow deposits. The
underlying plasma cell dyscrasia
responded to high - dose melpha-
lan followed by autologous stem
cell rescue. (b) Follow - up SAP
scintigraphy 3 years after
chemotherapy showed greatly
reduced uptake of tracer
indicating substantial regression
of her amyloid deposits. (Courtesy
of Professor P.N. Hawkins,
National Amyloidosis Centre,
Royal Free Hospital, London.) (a) (b)