Page 297 - Essential Haematology
P. 297
Chapter 21 Multiple myeloma and related disorders / 283
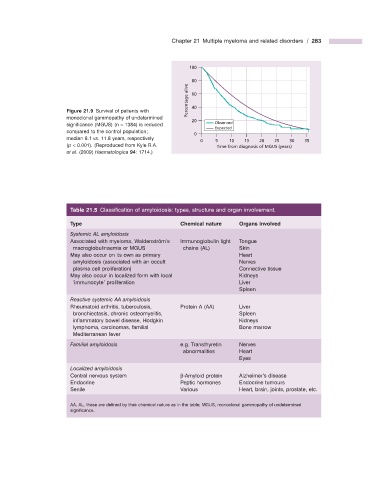
100
80
Percentage alive 60
Figure 21.9 Survival of patients with 40
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined
20
signifi cance (MGUS) (n = 1384) is reduced Observed
Expected
compared to the control population;
0
median 8.1 vs . 11.8 years, respectively
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
( p < 0.001). (Reproduced from Kyle R.A. Time from diagnosis of MGUS (years)
et al. (2009) Haematologica 94 : 1714.)
Table 21.5 Classifi cation of amyloidosis: types, structure and organ involvement.
Type Chemical nature Organs involved
Systemic AL amyloidosis
Associated with myeloma, Waldenstr ö m ’ s Immunoglobulin light Tongue
macroglobulinaemia or MGUS chains (AL) Skin
May also occur on its own as primary Heart
amyloidosis (associated with an occult Nerves
plasma cell proliferation) Connective tissue
May also occur in localized form with local Kidneys
‘ immunocyte ’ proliferation Liver
Spleen
Reactive systemic AA amyloidosis
Rheumatoid arthritis, tuberculosis, Protein A (AA) Liver
bronchiectasis, chronic osteomyelitis, Spleen
infl ammatory bowel disease, Hodgkin Kidneys
lymphoma, carcinomas, familial Bone marrow
Mediterranean fever
Familial amyloidosis e.g. Transthyretin Nerves
abnormalities Heart
Eyes
Localized amyloidosis
Central nervous system β - Amyloid protein Alzheimer ’ s disease
Endocrine Peptic hormones Endocrine tumours
Senile Various Heart, brain, joints, prostate, etc.
AA, AL, these are defi ned by their chemical nature as in the table; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined
signifi cance.